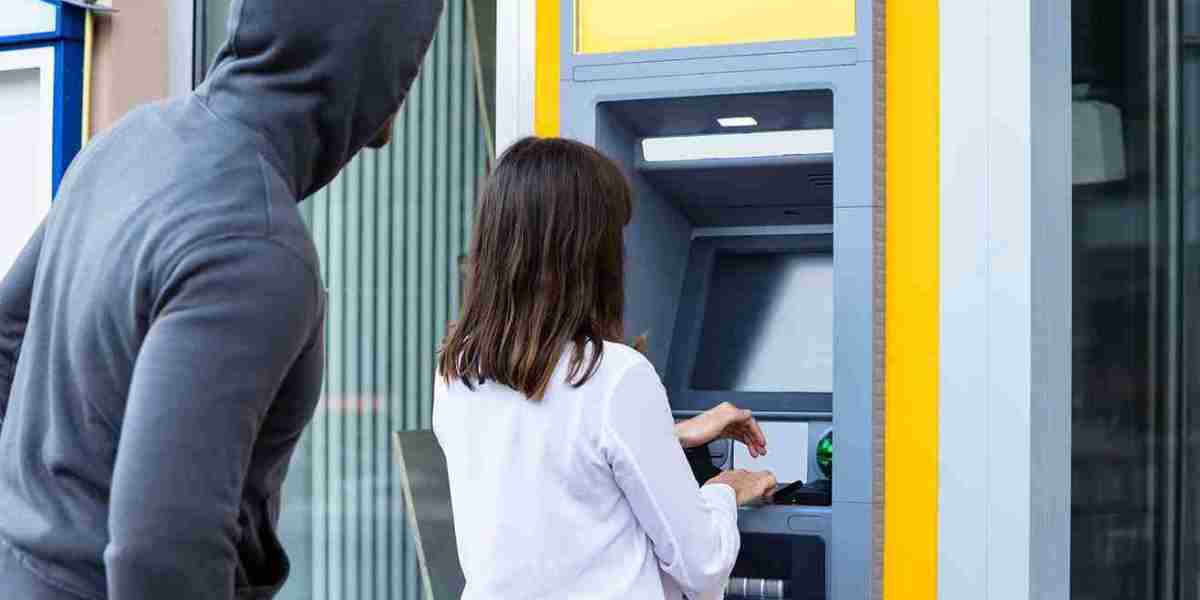
The ATM security market is a critical segment of the global financial services industry, ensuring secure and seamless transactions for millions of users worldwide. However, this market faces several significant challenges that hinder its growth, innovation, and effectiveness. Addressing these hindrances is essential to secure financial ecosystems and maintain public trust in banking systems. This blog explores the key barriers in the ATM security market and discusses the implications of these issues on industry players and end-users alike.
1. Rising Incidences of Cybercrime
One of the most pressing challenges for the ATM security market is the alarming increase in cybercrime. Hackers constantly devise sophisticated techniques to bypass security measures, leading to unauthorized access and significant financial losses. Skimming devices, malware attacks, and card cloning are becoming more prevalent, forcing ATM manufacturers and banks to continuously update their security protocols.
2. High Implementation Costs
Installing and maintaining advanced security solutions in ATMs is a costly endeavor. This includes expenses for hardware, software, and regular updates to ensure compliance with industry standards. Many smaller financial institutions find it challenging to allocate sufficient budgets for such investments, resulting in uneven security measures across the industry.
3. Integration Issues with Legacy Systems
A majority of ATMs still operate on outdated technologies, posing significant barriers to the integration of modern security solutions. Upgrading or replacing these systems is often a complex and time-consuming process, requiring extensive coordination between hardware manufacturers, software providers, and financial institutions.
4. Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
The ATM security market is heavily regulated, with stringent compliance requirements to protect consumers and safeguard financial transactions. While necessary, these regulations often pose hurdles for companies attempting to introduce innovative solutions. Balancing compliance with innovation remains a challenge, as any deviation can result in severe penalties or loss of market credibility.
5. Limited Awareness and Training
A significant barrier to effective ATM security is the lack of awareness and training among stakeholders, including bank staff and customers. Human errors, such as negligence in protecting PINs or failing to recognize suspicious devices, exacerbate security vulnerabilities. Enhanced training programs and awareness campaigns are essential to address this issue.
6. Dependence on Physical Security
Despite advancements in digital security, physical security remains a major concern for ATMs, especially in regions with high crime rates. Vandalism, theft, and physical attacks on ATMs continue to cause significant disruptions. Ensuring robust physical security measures, such as reinforced enclosures and 24/7 surveillance, is critical to maintaining operational integrity.
Implications of These Hindrances
The challenges in the ATM security market not only threaten the safety of financial transactions but also have broader implications. Increased incidences of fraud and theft undermine public confidence in ATM usage, potentially leading to reduced customer engagement and higher operating costs for banks. Moreover, these hindrances slow down technological advancements and the adoption of innovative solutions that could benefit the financial services ecosystem.
Steps to Mitigate Challenges
To overcome these barriers, stakeholders in the ATM security market must adopt a collaborative and proactive approach. This includes investing in cutting-edge security technologies, fostering partnerships with cybersecurity experts, and developing comprehensive regulatory frameworks that encourage innovation. Public awareness campaigns and industry-wide knowledge sharing are also vital to address gaps in training and awareness.
By tackling these challenges, the ATM security market can unlock new opportunities for growth and deliver safer, more reliable financial services to users worldwide.