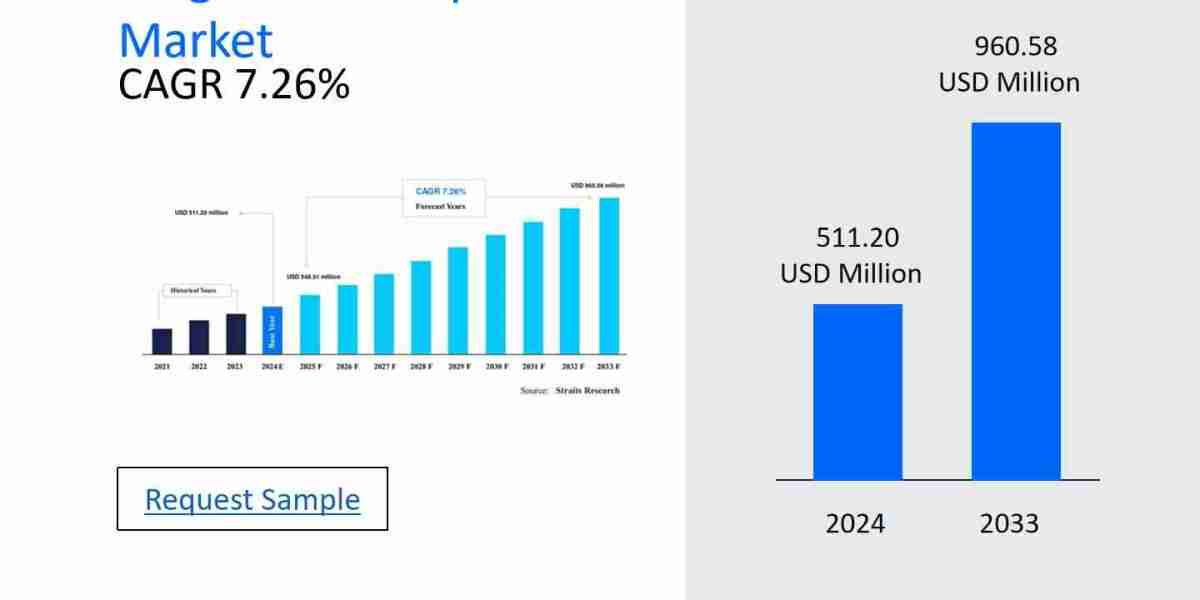
The ferro vanadium market has witnessed steady growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for high-strength steel alloys in industries such as automotive, construction, and energy. Ferro vanadium, which enhances the strength, durability, and corrosion resistance of steel, is essential for manufacturing components that meet modern engineering standards. However, despite its critical role, the market faces several barriers and pain points that hinder its growth potential. These obstacles, including price volatility, supply chain disruptions, and stringent environmental regulations, present challenges for market players. This article explores these hindrances in greater detail and examines the impact they have on the ferro vanadium industry.
Price Volatility
One of the most prominent barriers in the ferro vanadium market is the volatility of vanadium prices. Vanadium, the primary raw material used in the production of ferro vanadium, is subject to price fluctuations due to factors such as changes in global supply and demand, geopolitical tensions, and supply chain disruptions. The concentration of vanadium production in a few countries like China, South Africa, and Russia makes the market susceptible to external factors, such as trade restrictions or mining disruptions in these regions. These fluctuations create uncertainty for manufacturers and customers alike, complicating price forecasting and long-term planning.
Price instability also affects profitability. Ferro vanadium producers may face challenges in passing on higher costs to customers, especially in competitive markets where price sensitivity is a critical factor. This issue becomes more pronounced when the price of vanadium increases rapidly, forcing manufacturers to absorb costs or operate at a reduced margin. Consequently, price volatility remains one of the most significant pain points hindering growth in the ferro vanadium market.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain issues present another significant barrier to growth. Ferro vanadium is largely produced through vanadium mining and smelting, and these processes are concentrated in specific geographic regions. The reliance on a limited number of countries for vanadium supply makes the market vulnerable to external disruptions. Geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, or logistical challenges in these regions can lead to delays in production and distribution, causing disruptions in the supply of ferro vanadium.
Furthermore, the extraction and processing of vanadium are energy-intensive, and any supply interruptions in critical raw materials, such as energy, can exacerbate delays. Supply chain disruptions can also impact the cost structure of ferro vanadium producers, who may face higher transportation or logistics costs in the event of bottlenecks. For companies dependent on timely deliveries to meet customer demands, these disruptions can lead to lost business and a diminished reputation.
Environmental Regulations and Sustainability Pressures
Environmental regulations and sustainability pressures are increasingly becoming hindrances for the ferro vanadium market. The production of ferro vanadium is energy-intensive, and the growing emphasis on sustainability across industries has led to stricter environmental standards. Governments in major markets, particularly Europe and North America, are tightening regulations on carbon emissions and mandating the adoption of cleaner, more energy-efficient technologies. Ferro vanadium producers that fail to comply with these regulations may face penalties, fines, or operational shutdowns, which can severely affect profitability.
In addition, the market is facing increasing scrutiny regarding the environmental impact of vanadium mining. As the extraction of vanadium requires significant resources and energy, environmentalists and stakeholders are pushing for more sustainable practices. This includes the adoption of cleaner production methods and the increased recycling of vanadium from used steel. While these initiatives are beneficial in the long run, they require substantial investments in research and development, technology, and infrastructure, presenting a barrier to growth for smaller or less financially stable companies in the market.
Limited Availability of Vanadium Resources
Vanadium is not as abundant as other metals, which makes its extraction a more complex and costly process. Despite its critical role in the production of ferro vanadium, the global supply of vanadium is limited, and the metal is mostly sourced from a few countries. This restricted availability can lead to supply shortages, further driving up prices. The market’s reliance on primary sources of vanadium leaves it vulnerable to resource depletion and fluctuating production rates.
The limited availability of vanadium resources also contributes to the market’s dependence on mining. This presents challenges from an environmental standpoint, as vanadium mining requires extensive land use and can result in habitat destruction and other environmental issues. Efforts to expand recycling and alternative sourcing options have been somewhat successful, but they are not yet enough to significantly reduce the market’s dependence on primary mining.
Technological Barriers
Although the ferro vanadium industry has seen innovations in production and recycling technologies, the adoption of these advancements can be slow and costly. Developing new technologies to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact requires substantial financial investment. Smaller producers, in particular, may lack the capital to invest in advanced technologies, which can lead to a technological divide between larger and smaller companies.
Moreover, while the industry has made strides in vanadium recycling, the processes for efficiently reclaiming vanadium from used steel are still being refined. The capacity for large-scale recycling of vanadium is not yet sufficient to meet global demand, and scaling up these efforts presents significant technical and economic challenges.
Conclusion
The ferro vanadium market faces multiple barriers that hinder its growth potential, including price volatility, supply chain disruptions, environmental regulations, and technological challenges. These pain points create an environment of uncertainty and risk for producers, customers, and stakeholders. Despite these challenges, the market is also undergoing significant innovations, including advancements in recycling technologies and energy-efficient production methods. Addressing the barriers through strategic investments in sustainable practices, diversified supply chains, and technological improvements can help overcome these hindrances and position the ferro vanadium market for continued growth in the years ahead.