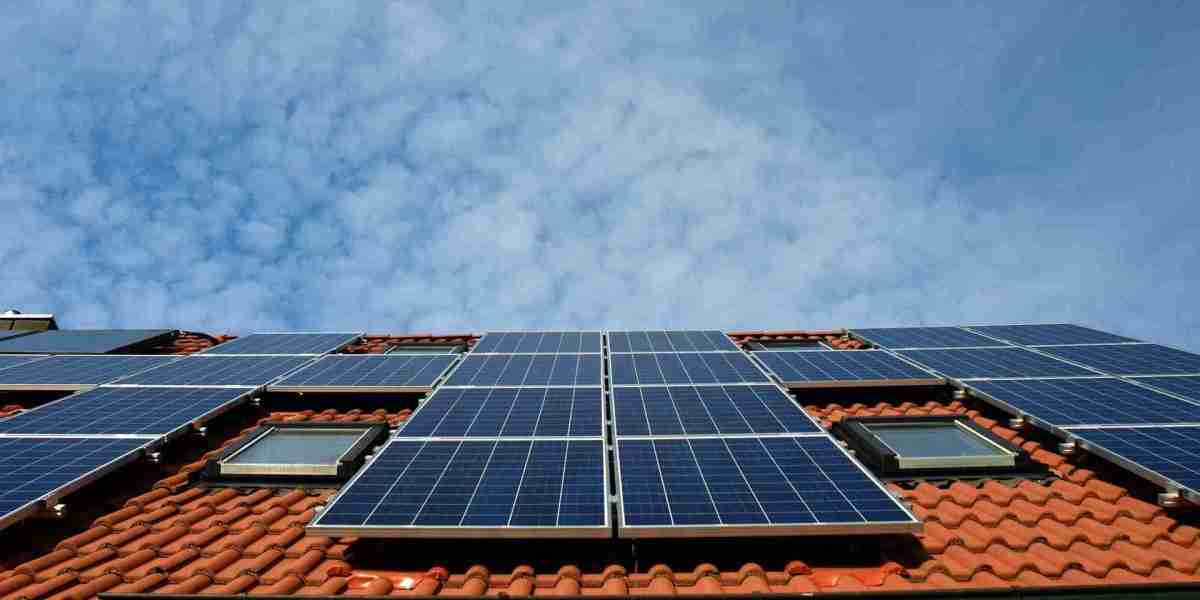
The PV Solar Market has gained significant momentum over the past decade, driven by growing environmental concerns and the global shift towards renewable energy. Despite its potential, the industry faces numerous challenges that hinder its growth and widespread adoption. This article explores the primary hurdles facing the PV solar market and the strategies that can be employed to mitigate these challenges.
High Initial Capital Costs
One of the most significant challenges in the PV solar market is the high upfront cost of installing solar panels. While the cost of solar technology has decreased over time, it still requires considerable investment, especially for large-scale projects. This financial barrier can be discouraging for both individuals and businesses, particularly in regions with limited access to financing options. To address this issue, various financing mechanisms such as government incentives, tax rebates, and low-interest loans can make solar adoption more affordable. Additionally, advancements in solar technology are expected to lower costs, making it more accessible to a wider audience.
Intermittency and Energy Storage Limitations
Solar power, by its nature, is intermittent and dependent on weather conditions. This creates challenges in maintaining a consistent and reliable energy supply, especially in regions with variable sunlight hours. The need for energy storage systems to store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during cloudy periods has created a bottleneck in the market. While battery storage solutions have made significant progress, they remain expensive and often lack the capacity to meet large-scale energy demands. Developing cost-effective, high-capacity storage solutions is essential for overcoming this challenge. Additionally, improving the grid infrastructure to integrate solar power effectively will help in balancing supply and demand.
Land and Space Constraints
Another challenge facing the PV solar market is the availability of land or space for large solar installations, especially in densely populated urban areas. The competition for land use between agriculture, housing, and industry can limit the amount of space available for solar farms. In some regions, land acquisition for solar projects can be a lengthy and complex process, involving zoning laws, land rights issues, and community opposition. One potential solution is the use of rooftop solar installations, which can provide an alternative to large land-based solar farms. Additionally, integrating solar panels into existing infrastructure, such as roads, highways, and buildings, could help mitigate land constraints.
Regulatory and Policy Barriers
The regulatory environment is another significant hurdle for the PV solar market. In many regions, policies that support solar energy are either inadequate or inconsistently enforced. This lack of clear and stable regulations can create uncertainty for investors and developers. Moreover, regulatory barriers such as complex permitting processes, interconnection issues, and grid access restrictions can slow down the deployment of solar systems. To address these issues, governments need to streamline regulations and create supportive policies that promote solar energy adoption. This includes incentives for research and development, subsidies for consumers, and removing barriers to grid integration.
Supply Chain and Material Shortages
The PV solar market depends on the availability of raw materials such as silicon, aluminum, and rare earth metals. Any disruptions in the supply chain, whether due to geopolitical factors, natural disasters, or resource limitations, can impact the production and cost of solar panels. The growing demand for solar technology can strain the supply chain, leading to delays in manufacturing and price volatility. To overcome this challenge, the industry must diversify its supply sources and invest in developing more efficient manufacturing processes. Additionally, increasing the recycling of materials from old solar panels could help mitigate the pressure on raw material resources.
Public Perception and Awareness
Despite the growing recognition of the environmental benefits of solar energy, public perception and awareness remain significant barriers. Many people still view solar energy as an expensive and unreliable energy source. Misconceptions about the effectiveness of solar technology, its maintenance needs, and its long-term benefits can discourage potential adopters. To address these concerns, it is crucial to educate the public about the advantages of solar energy and provide clear information about the technology's reliability and financial benefits. Public awareness campaigns and outreach programs can play a vital role in overcoming these perception barriers.
Grid Integration Challenges
Integrating solar power into the existing energy grid poses technical challenges. The decentralized nature of solar power generation requires upgrades to grid infrastructure to accommodate the variable nature of solar generation. The current grid system in many countries is not equipped to handle the fluctuations in solar energy production, leading to inefficiencies and potential power outages. Investment in smart grid technologies, energy storage systems, and improved grid management practices will be necessary to ensure a stable and reliable electricity supply.
Conclusion
The PV solar market has the potential to revolutionize the global energy landscape, but it faces several challenges that must be addressed. Overcoming high upfront costs, intermittency issues, land constraints, regulatory barriers, and supply chain disruptions will require coordinated efforts from governments, businesses, and consumers. By implementing the right mitigation strategies and continuing to innovate in solar technology, the PV solar market can overcome these hurdles and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.