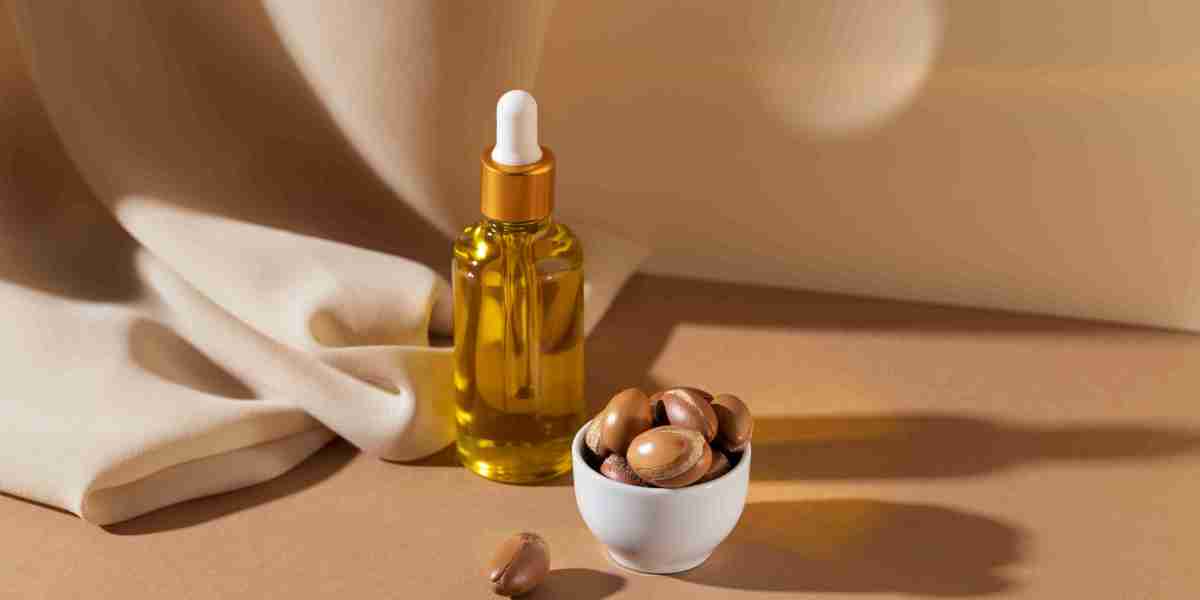
Argan oil, derived from the seeds of the Argan tree native to Morocco, has gained significant popularity worldwide due to its health benefits and use in cosmetics and food products. As the global demand for this natural oil continues to grow, the argan oil market faces various challenges that impact its expansion. These challenges are largely influenced by environmental, economic, and regulatory factors, all of which play a critical role in shaping the future of the industry.
Environmental Challenges
The Argan oil market is heavily dependent on the cultivation of Argan trees, which thrive in specific ecological conditions found primarily in Morocco's semi-arid regions. Environmental factors such as climate change, deforestation, and water scarcity have increasingly become obstacles to the sustainable production of Argan oil.
Climate change, particularly rising temperatures and unpredictable rainfall patterns, directly affects the growth and productivity of Argan trees. These trees, known for their resilience in harsh environments, are nonetheless vulnerable to extreme weather conditions. Droughts, a growing concern due to climate change, can severely limit the water supply necessary for the trees' survival, thus impacting the yield of Argan nuts.
Deforestation also poses a significant threat to the Argan oil market. With the growing demand for land for agriculture and urbanization, the Argan tree's natural habitat has been encroached upon, resulting in a reduction of Argan forests. Efforts to combat deforestation and protect the Argan tree's ecosystem have been underway, but continued vigilance and conservation efforts are critical for the long-term sustainability of the Argan oil market.
Economic Challenges
The Argan oil market is intricately linked to the economic conditions of Morocco, where the majority of Argan oil production takes place. The economic challenges faced by the country, such as fluctuating market prices, infrastructure limitations, and unemployment, can significantly influence the supply chain and production capacity of Argan oil.
The global demand for Argan oil has led to increased competition, with various countries vying for a share of the market. This has resulted in price fluctuations, especially in the face of limited supply and increasing demand. As Argan oil is a labor-intensive product, the price of production is highly sensitive to changes in wages and labor costs, which in turn affect the market price of Argan oil. Furthermore, the lack of sufficient infrastructure in rural areas of Morocco where Argan trees grow hampers the efficient transportation and processing of the oil, further contributing to production costs.
Another economic challenge is the potential for the exploitation of Argan oil producers. While the industry provides important income for rural populations, especially women who are often involved in the labor-intensive process of extracting the oil, there are concerns regarding fair wages and working conditions. Ensuring that the economic benefits of Argan oil are distributed equitably remains a key issue for stakeholders in the market.
Regulatory Challenges
The regulatory landscape surrounding the Argan oil market is another critical factor influencing the growth and expansion of the industry. Regulations related to product quality, sustainability, and fair trade play a vital role in shaping the practices of Argan oil producers and exporters.
One of the most significant regulatory challenges is ensuring the authenticity and purity of Argan oil. With the rise in popularity of Argan oil, there has been an increase in counterfeit and adulterated products entering the market. This undermines consumer trust and damages the reputation of genuine Argan oil producers. To combat this, Moroccan authorities, alongside international regulatory bodies, have implemented stricter certification standards to ensure that only pure and authentic Argan oil reaches consumers. These measures include establishing origin labels and certification programs, but enforcement remains a challenge in the face of global demand.
Sustainability is another regulatory concern. Argan oil production, while beneficial to local communities, must be managed in a way that does not lead to overexploitation of natural resources. In response, the Moroccan government and environmental organizations have introduced regulations aimed at protecting the Argan tree and its ecosystem. These include restrictions on logging, efforts to restore degraded land, and promoting sustainable farming practices that minimize environmental impact.
Additionally, international trade regulations, including tariffs and export restrictions, also affect the flow of Argan oil to global markets. Changes in trade policies or geopolitical tensions can disrupt supply chains and influence the competitiveness of Moroccan Argan oil on the international stage.
Conclusion
The Argan oil market is influenced by a combination of environmental, economic, and regulatory factors that affect its growth and sustainability. While the demand for Argan oil continues to rise, the industry faces significant challenges in maintaining the balance between production and sustainability. Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort from governments, producers, and consumers to ensure that the Argan oil market can thrive without compromising the environment or the livelihoods of those who depend on it.
As the market continues to expand, it is crucial to focus on sustainable practices, fair economic conditions, and robust regulations to secure the future of Argan oil production, ensuring that it remains a valuable resource for generations to come.