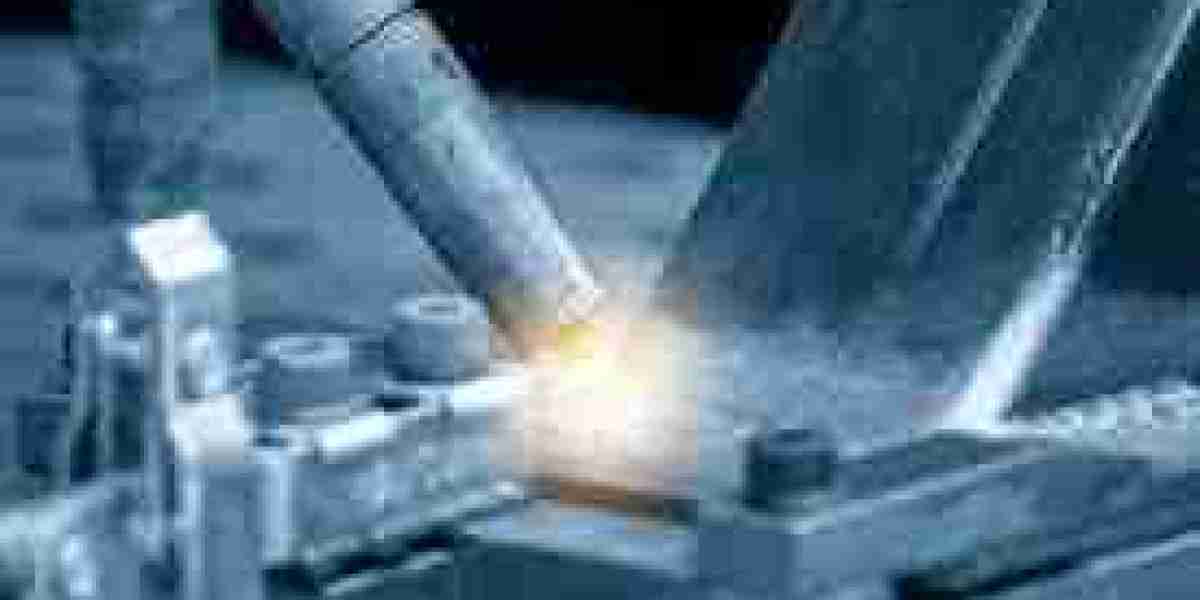
The Laser Welding Machine Market is gaining momentum, driven by robust infrastructure growth in developing manufacturing hubs. As emerging economies expand their industrial bases and modernize production facilities, the demand for precise, efficient, and advanced welding technologies is on the rise.
Infrastructure Boom Driving Industrial Investment
Emerging markets such as India, Vietnam, Indonesia, Brazil, and several African nations are experiencing significant infrastructure development. Governments are investing heavily in industrial parks, transportation networks, smart cities, and energy projects to stimulate economic growth and attract foreign direct investment.
This expansion creates a strong demand for high-performance manufacturing equipment, including laser welding machines. These machines are increasingly viewed as essential tools in modern infrastructure development due to their ability to deliver strong, precise welds with minimal defects and downtime.
From steel structures and bridges to pipelines and factory machinery, laser welding plays a crucial role in creating high-integrity components that support long-term infrastructure reliability.
Rise of Localized Manufacturing and Automation
Developing regions are not just building infrastructure—they are also actively promoting localized manufacturing. Many countries are offering incentives for domestic production in sectors like automotive, electronics, appliances, defense, and renewable energy.
As factories are built from the ground up, manufacturers are investing in modern production tools rather than legacy systems. Laser welding machines offer a perfect fit for these new facilities, thanks to their efficiency, low maintenance, and integration capabilities with automated lines.
The availability of CNC-based and robot-integrated laser welding systems allows factories in emerging regions to match global standards from the start, giving them an edge in international markets.
Sectors Benefiting from Infrastructure-Driven Demand
Construction and heavy equipment: The demand for construction vehicles, cranes, and earthmovers has increased alongside road and housing development. Laser welding ensures strong joints in load-bearing components while reducing manufacturing cycle times.
Energy and utilities: Infrastructure growth includes pipelines, refineries, and renewable energy plants. Laser welding is widely used in creating durable pipe welds, turbine parts, and structural mounts for solar panels and wind turbines.
Transportation and railways: Rail and metro expansion projects require components like car bodies, tracks, and couplings to be manufactured with high precision. Laser welding provides the clean, strong joints needed for long-term reliability and safety.
Consumer appliances and electronics: As regional production facilities emerge, local manufacturers are investing in high-precision welding for air conditioners, refrigerators, and electronic goods to meet growing consumer demand.
Competitive Advantages for Emerging Markets
Laser welding helps emerging manufacturing hubs become more competitive globally. By adopting advanced equipment early, companies can:
Improve product quality to match international standards
Minimize defects and costly rework
Reduce labor dependency with automated solutions
Lower production waste and energy use
Increase throughput to meet export volumes
These advantages support both economic development and global competitiveness, which are key priorities for many governments in emerging economies.
Government Policies and Industrial Programs
Many developing countries are supporting industrial growth with favorable policies, infrastructure spending, and investment in technology parks. Programs like India’s “Make in India,” Vietnam’s “Industry 4.0” vision, and Brazil’s national innovation plans all encourage modernization in manufacturing.
Laser welding machines are among the technologies supported through grants, tax credits, and technology incubation centers. In some regions, import duties on high-tech manufacturing equipment have also been lowered to make adoption easier for local manufacturers.
These policy measures are contributing to the fast-paced adoption of laser-based welding systems across emerging markets.
Growth of Domestic Machine Builders and Integrators
While large global players still dominate the high-end segment, many local companies in Asia, South America, and Eastern Europe are beginning to produce affordable laser welding machines tailored to regional needs.
These domestic manufacturers often provide cost-effective systems optimized for local materials, workforce capabilities, and power infrastructure. As a result, smaller companies are now able to access laser welding technology without relying solely on imports.
Furthermore, local integrators are customizing solutions by combining global laser modules with locally built motion systems, creating hybrid products that fit local budgets and applications.
Challenges in Adoption and Overcoming Barriers
Although interest is growing rapidly, some barriers still exist:
Limited awareness: In smaller cities and towns, manufacturers may not be fully aware of laser welding benefits.
Skilled labor shortage: Operators and maintenance staff may lack experience with advanced machines.
High upfront costs: Initial investment may be steep for small and mid-sized businesses.
To address these challenges, equipment providers are partnering with local training institutions, offering on-site demos, and launching rental or leasing options. As adoption grows, knowledge and cost barriers are expected to decrease significantly.
Outlook for Continued Market Expansion
As infrastructure and industrial ecosystems continue to grow in emerging markets, so too will the demand for laser welding machines. These machines are proving to be long-term assets, offering both operational efficiency and compliance with international production standards.
In the coming years, adoption is likely to grow not just in large manufacturing hubs, but also in tier-2 and tier-3 cities where smaller units are being established to serve regional needs. Portable, compact, and CNC-controlled laser welders will particularly see increased usage in these decentralized manufacturing setups.
Conclusion
The laser welding machine market is being fuelled by the infrastructure growth and manufacturing expansion in emerging global hubs. With rising investment in modern factories, domestic production capabilities, and advanced automation, these regions are embracing laser welding technologies at a fast pace. As this trend continues, laser welding will play a vital role in shaping the next generation of efficient, competitive, and sustainable industrial economies.