The global Utility Asset Management Market is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological innovations, increasing regulatory mandates, and growing demands for efficient utility operations. As energy consumption continues to rise and utility infrastructures age, effective asset management has become vital to ensure system reliability, reduce operational costs, and maintain compliance with environmental and safety standards.
Rising Need for Infrastructure Modernization
Aging utility infrastructure, particularly in developed economies, is a major challenge that calls for proactive asset management. Power grids, water pipelines, and gas distribution networks in many countries are decades old, increasing the risk of failure and service disruptions. Utility asset management plays a critical role in identifying vulnerable assets, scheduling maintenance, and extending the life span of existing infrastructure through predictive analytics and condition-based monitoring.
Developing nations, on the other hand, are rapidly expanding their utility networks to meet the growing needs of urbanization and industrialization. This expansion creates opportunities to implement modern asset management systems from the outset, thereby ensuring long-term operational efficiency and cost savings.
Technology Driving Market Growth
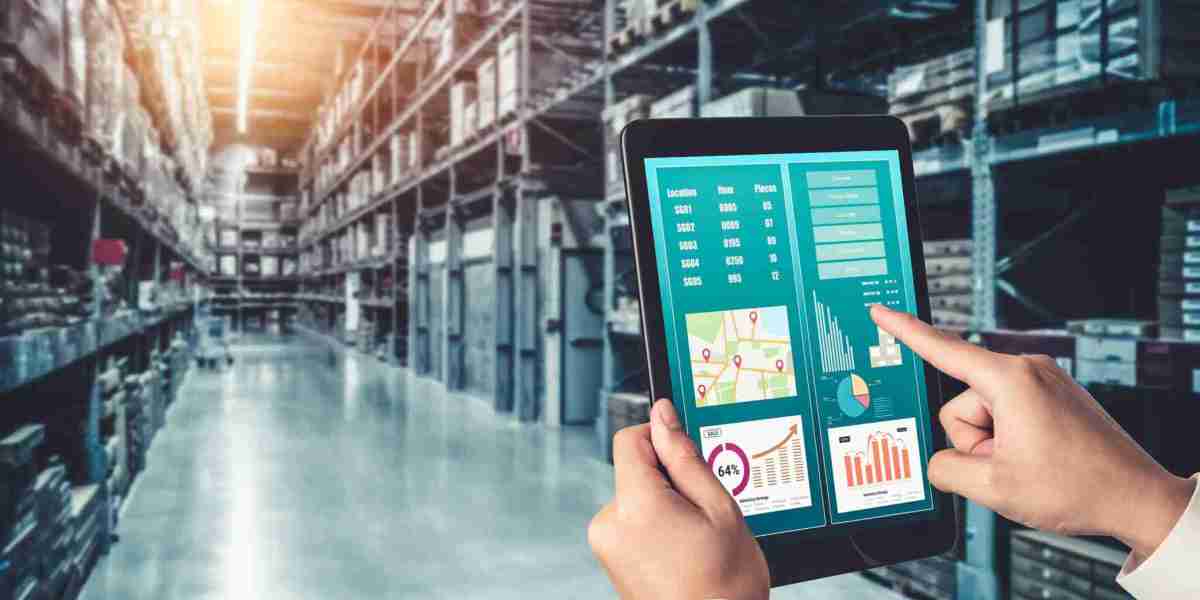
The integration of advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), Geographic Information Systems (GIS), and cloud computing is revolutionizing the way utilities manage their assets. These technologies facilitate real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making.
IoT-enabled sensors, for instance, can collect real-time data on asset performance, while AI algorithms analyze this data to predict failures or maintenance needs. GIS tools provide spatial insights into asset location, condition, and accessibility, enabling utilities to respond faster to outages or emergencies. Moreover, cloud platforms offer scalable data storage and access, improving collaboration among utility departments and external stakeholders.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Pressures
Governments and regulatory bodies across the globe are implementing stringent guidelines for asset safety, environmental impact, and service reliability. These regulations mandate utilities to adopt systematic asset management practices. For example, frameworks such as ISO 55000 provide standardized approaches to asset management, focusing on value realization, risk mitigation, and continual improvement.
In regions like North America and Europe, regulators are increasingly linking rate approvals and funding to utilities' ability to demonstrate robust asset management plans. This regulatory push is encouraging utilities to invest in advanced asset management systems to ensure compliance and secure financial incentives.
Utility Segments Fueling Demand
The Utility Asset Management Market spans across electricity, water, and gas sectors, with each segment having unique requirements and challenges.
Electricity: The shift toward renewable energy and decentralized power generation is adding complexity to grid operations. Asset management ensures grid resilience and efficient integration of new energy sources.
Water: Climate change and water scarcity are pushing utilities to manage aging water distribution systems more effectively, reduce leakage, and improve conservation.
Gas: Gas utilities face stringent safety regulations, making pipeline integrity management a top priority.
Asset management systems customized to each utility type help optimize resource allocation, improve uptime, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Challenges Hindering Full-Scale Adoption
Despite the benefits, several challenges impede the widespread adoption of utility asset management solutions. High implementation costs, data integration issues, and resistance to change among field personnel are key obstacles. Small and medium utilities, especially in developing regions, may lack the financial and technical resources to adopt comprehensive systems.
Additionally, cybersecurity risks associated with connected asset management platforms pose another layer of concern. As utilities digitize their operations, protecting data from breaches and ensuring secure communications becomes critical.
Market Outlook and Future Opportunities
The Utility Asset Management Market is poised for robust growth in the coming years, driven by increasing infrastructure investments, rising energy demand, and the global transition toward smart utilities. Vendors are focusing on delivering scalable, interoperable, and user-friendly platforms that cater to the specific needs of diverse utility providers.
Collaborations between technology providers and utility companies are expected to accelerate innovation, offering integrated solutions that combine asset management with energy management, sustainability tracking, and customer engagement tools.
Furthermore, as governments promote green energy and resilient infrastructure development through stimulus programs and policy support, utility companies are expected to scale up their asset management efforts. The emphasis will likely shift from reactive maintenance to strategic, lifecycle-oriented asset optimization.
Conclusion
The Utility Asset Management Market is evolving rapidly to meet the dual demands of modernization and efficiency. By embracing digital technologies, adhering to regulatory frameworks, and adopting proactive asset strategies, utilities can ensure infrastructure resilience and long-term sustainability. As the energy and utility landscape becomes increasingly complex, asset management will remain a cornerstone of operational excellence and strategic growth.