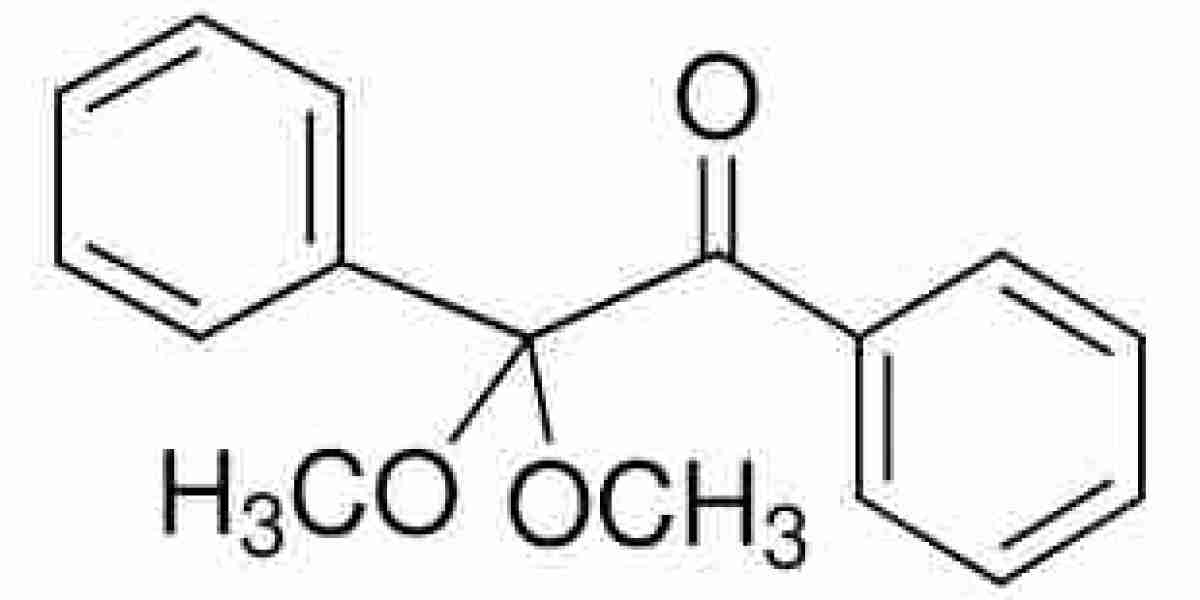
The Electrical Steel Market is experiencing structural transformation as global policies and environmental mandates drive sweeping changes in supply chain strategies. With energy efficiency and sustainability becoming central to industrial planning, manufacturers of electrical steel—essential in motors, transformers, and generators—are being compelled to adapt every aspect of their sourcing, production, and distribution models.
Regulatory Pressure for Low-Carbon Production
Environmental regulations have become a decisive factor in shaping the operational landscape for electrical steel producers. International agreements such as the Paris Climate Accord, the European Green Deal, and region-specific frameworks like China’s dual carbon goals are pushing manufacturers toward decarbonized operations. These mandates are no longer aspirational; they are being enforced through carbon pricing, emissions reporting requirements, and green procurement policies.
Electrical steel, though critical for energy-efficient applications, is energy-intensive to produce. As such, regulatory authorities are closely examining emissions across its entire lifecycle—from iron ore extraction to final annealing. Producers are responding by investing in low-emission technologies such as hydrogen-based direct reduced iron (DRI) and electric arc furnaces powered by renewable energy. These shifts are not only regulatory responses but also strategic differentiators in an increasingly climate-conscious marketplace.
Green Procurement and Compliance-Driven Sourcing
One of the most significant impacts of environmental mandates is the pressure on procurement practices. Governments and major buyers, particularly in Europe and North America, are introducing green public procurement criteria that favor low-carbon materials. As a result, electrical steel producers are required to prove environmental compliance through carbon footprint disclosures, life cycle assessments, and third-party certifications such as Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs).
This shift is driving the need for traceable and sustainable raw material sourcing. Producers are revisiting their relationships with upstream suppliers, demanding transparency and environmental accountability. For example, mining operations supplying iron ore and alloys are being assessed not just on cost and volume but on their water usage, land impact, and emissions intensity. This extends to secondary material sourcing as well, where recycled steel content is gaining favor for reducing embodied carbon.
Localization and Resilient Supply Chains
Supply chain resilience has emerged as a strategic focus area following global disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions. Environmental policies are adding another layer of urgency to reconfigure global sourcing and production networks. To mitigate carbon footprints and reduce exposure to volatile cross-border logistics, many electrical steel manufacturers are adopting localization strategies.
Localizing supply chains enables companies to shorten transportation routes, thereby reducing emissions from shipping and freight. It also aligns with rising protectionist policies that favor domestic manufacturing and sourcing—especially in critical sectors like energy infrastructure and electric vehicles, where electrical steel plays a pivotal role.
Companies are investing in new regional production hubs that meet local environmental compliance standards. For instance, several leading manufacturers are establishing or expanding facilities in the U.S. and India to serve their growing markets while reducing the environmental cost of long-distance transportation from Asia or Europe.
Circular Economy Initiatives and Waste Reduction
Environmental mandates are also promoting circular economy principles across the electrical steel value chain. Regulators are pushing industries to reduce waste generation and improve material recovery rates. In response, manufacturers are enhancing scrap utilization in their processes. Using recycled steel not only reduces dependency on virgin materials but also significantly lowers energy use and emissions.
Furthermore, innovations in waste heat recovery, water recycling, and closed-loop production are helping manufacturers reduce their environmental impact while boosting operational efficiency. Several steelmakers are piloting programs to reclaim spent insulation coatings and improve yield ratios during rolling and slitting operations, minimizing material loss at every stage.
Packaging, Logistics, and End-of-Life Considerations
Downstream supply chain elements are also being restructured under the lens of environmental compliance. Packaging materials, for instance, are shifting from plastic to biodegradable or recyclable alternatives. Logistics providers are being selected based on their ability to provide low-emission freight solutions, such as rail over truck transport or electrified fleet options.
At the other end of the chain, manufacturers are working with OEMs and end-users to design products with end-of-life recyclability in mind. Electrical steel grades are being optimized to facilitate easier disassembly and material recovery from decommissioned motors and transformers, in alignment with circular economy targets.
Challenges in Balancing Cost and Compliance
Despite the positive momentum, adapting to these policies and mandates presents significant challenges. The transition to greener production technologies often involves high upfront costs and technical complexities. Many mid-sized producers, especially in emerging markets, lack the capital or know-how to meet new environmental benchmarks, putting them at risk of market exclusion.
Moreover, complying with multiple overlapping regulations across different countries can increase complexity. A material certified for one region may not meet the standards of another without additional testing, documentation, or process changes. This drives up administrative costs and delays time-to-market, especially in global distribution scenarios.
Strategic Outlook and Competitive Advantage
Looking ahead, the ability to align with environmental mandates will increasingly determine a company’s competitiveness in the electrical steel market. Manufacturers that lead in low-emission production, sustainable sourcing, and regulatory compliance will gain access to premium markets and benefit from favorable financing, partnerships, and customer loyalty.
Sustainability is no longer a secondary concern; it is central to product differentiation and business continuity. Companies are integrating ESG considerations into core business strategies, including long-term supply agreements, technology investments, and stakeholder engagement. Innovations such as digital supply chain monitoring and blockchain-enabled material tracking are further strengthening transparency and accountability.
As climate policies become more rigorous, the electrical steel market must continue evolving. Strategic adaptation to environmental mandates will not only help companies meet regulatory requirements but also unlock new opportunities in emerging applications, from smart grids to electric mobility. In doing so, they will not only ensure compliance but also position themselves as enablers of the global energy transition.