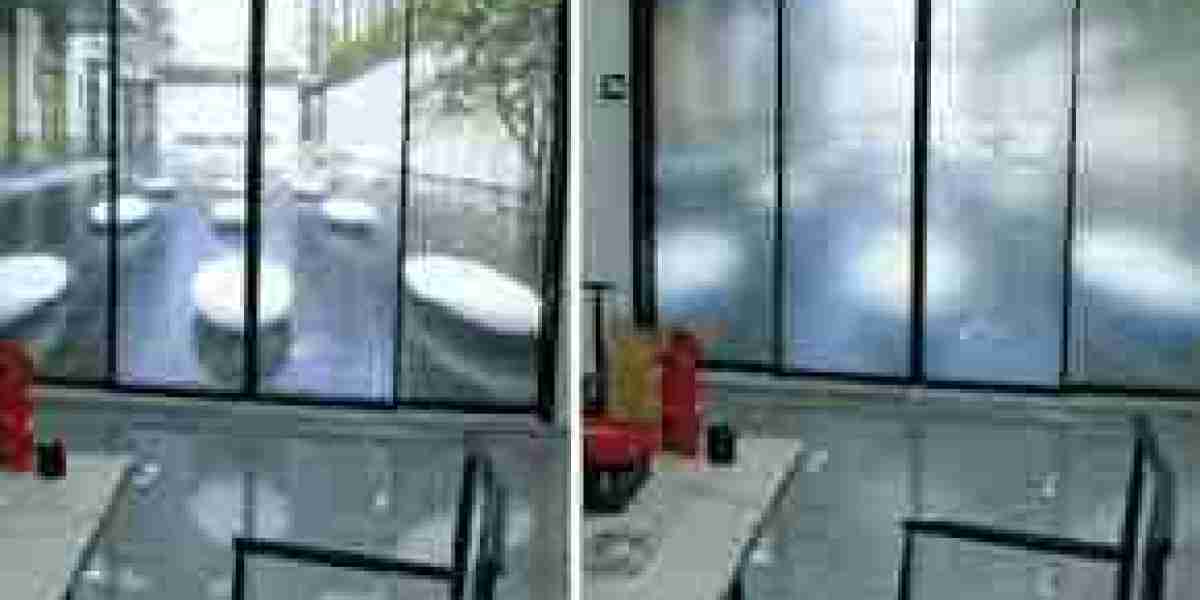
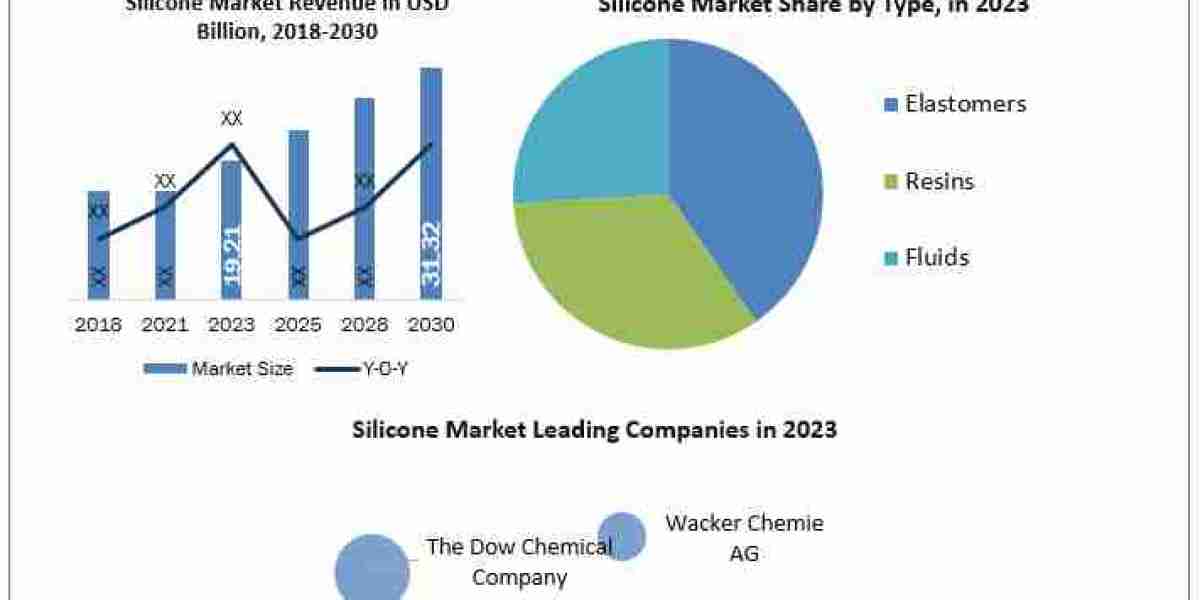
The residential and commercial smart glass market report highlights a transformative trend—urban design preferences are rapidly shifting to favor smart, dynamic materials such as smart glass. In the context of growing urban populations, environmental awareness, and the rise of intelligent infrastructure, cities are embracing design solutions that are functional, sustainable, and technologically advanced. Smart glass sits at the intersection of these requirements, making it a sought-after element in both new developments and retrofit projects across the globe.
Urban Design’s Paradigm Shift
Modern urban design is no longer centered solely on maximizing space or aesthetics. Today’s priorities include energy efficiency, adaptability, environmental harmony, and user-centric design. Smart glass aligns with these ideals by offering dynamic control over light, glare, and heat—key considerations in densely built environments.
Architects and planners are increasingly turning to smart glazing to create healthier indoor environments, reduce building energy footprints, and enhance urban aesthetics. The ability to design buildings with responsive façades or transform internal layouts with switchable partitions marks a significant leap in urban innovation.
Compact Cities, Smart Solutions
As cities become more compact, the built environment must work harder to deliver comfort, privacy, and sustainability. Traditional static glazing offers limited flexibility in controlling internal lighting or temperature. Smart glass, by contrast, enables real-time adaptation to external conditions, optimizing thermal performance and visual comfort without sacrificing natural light or views.
In high-density urban settings, this adaptability improves livability in residential towers and commercial buildings alike. Smart windows help mitigate urban heat islands, reduce cooling loads, and increase usable daylight, which is increasingly valued in vertical living environments.
Responsive Design in High-Rise Architecture
Urban skylines are dominated by high-rise buildings, where light control and solar management are critical. Smart glass is now a strategic component in designing towers that are not only structurally advanced but also responsive to environmental stimuli. Electrochromic or SPD smart glass allows building façades to transition smoothly between transparency and tint, reducing glare and solar gain on demand.
This capability enhances occupant experience in luxury condos, office buildings, and mixed-use spaces—improving tenant satisfaction while reducing reliance on HVAC systems. Smart façades are being adopted as symbols of modernity and sustainability in major global cities like New York, London, Singapore, and Dubai.
Balancing Transparency and Privacy
Changing urban design preferences also emphasize transparency—physically and metaphorically. Open-plan concepts, floor-to-ceiling glass, and panoramic views have become popular. However, these design elements pose challenges around glare and privacy. Smart glass offers the perfect balance, allowing for transparent aesthetics without compromising privacy.
In both residential and commercial buildings, smart partitions and switchable windows enhance spatial flexibility. A glass wall in a conference room can turn opaque at the touch of a button. In apartments, balconies and shower enclosures can offer both openness and discretion, aligning with evolving design expectations.
Biophilic and Wellness-Oriented Design
Urban design is becoming more wellness-oriented. Daylighting, visual comfort, and natural rhythms are integral to biophilic design—a concept gaining momentum in both homes and workplaces. Smart glass supports these principles by maximizing daylight access while reducing discomfort from heat and glare.
In healthcare facilities, schools, and wellness centers, dynamic glazing contributes to circadian rhythm regulation and psychological well-being. These benefits are now widely recognized, prompting urban planners to incorporate smart glass in environments where occupant health is prioritized.
Integration with Smart Building Ecosystems
Smart glass is increasingly integrated into broader smart building systems. Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled buildings can sync smart windows with occupancy sensors, HVAC systems, and lighting controls. Urban design now prioritizes such integration, especially in new districts planned as “smart cities.”
Smart glass that automatically adjusts based on indoor activity or time of day reflects the desire for seamless human-environment interaction. From energy dashboards to smartphone-controlled shading, urban dwellers want buildings that think, learn, and respond.
Aesthetic Flexibility and Architectural Freedom
One of the driving factors behind the use of smart glass in modern urban design is the freedom it provides to architects. Its adaptability means that buildings no longer have to choose between transparency and performance. Curved glass, frameless panels, and large-format glazing now feature smart functionality without compromising form.
Smart glass contributes to iconic building designs, allowing urban landscapes to reflect both tradition and innovation. Cities keen to showcase futuristic infrastructure—such as Tokyo, Shanghai, and Doha—are leading adopters of this material.
Urban Retrofitting for Sustainability
In addition to new constructions, older urban buildings are being retrofitted with smart technologies to meet updated environmental standards. Retrofitting with smart glass allows property owners to reduce energy consumption, improve occupant comfort, and modernize building aesthetics—without the need for full-scale demolition.
Cities worldwide offer incentives for such retrofits as part of climate action plans and urban renewal programs. Smart glass is especially useful in historic districts where exterior modifications must be minimal, but interior upgrades are encouraged.
Global Markets Aligning with Design Preferences
North America: Emphasis on smart city infrastructure and LEED-certified buildings has driven adoption in major metropolitan hubs.
Europe: High standards for energy efficiency and urban sustainability are aligning perfectly with the capabilities of smart glass.
Asia-Pacific: Rapid urbanization and government-backed intelligent infrastructure projects have made cities in China, India, and South Korea major growth areas.
Middle East: Ambitious architectural projects in Dubai, Riyadh, and beyond are integrating smart glazing to manage desert climate challenges stylishly.
Conclusion
The residential and commercial smart glass market is evolving in tandem with a global rethinking of how cities are designed. Changing urban design preferences—marked by the desire for sustainability, transparency, responsiveness, and wellness—are pushing smart glass from a niche innovation to a core building element.
As architects, urban planners, and developers strive to build smarter cities, smart glass provides an adaptable, elegant, and environmentally responsible solution. It empowers buildings to respond to their environment, reflect human needs, and elevate design to meet the demands of 21st-century urban life.
#smartglass #urbanarchitecture #buildingdesign #sustainablecities #smartbuildings #architecturaltrends #glassinnovation #greenurbanism #residentialdesign #commercialinteriors #futureofcities #dynamicglazing