The Hair Restoration Market is a multifaceted ecosystem involving research, manufacturing, clinical services, digital marketing, and post-treatment care. To understand how this industry functions effectively, a detailed value chain analysis reveals the interdependencies among its various stakeholders—from innovative product developers to clinics and end-users. As the demand for both surgical and non-surgical hair restoration grows globally, companies must optimize each link of the value chain to deliver high-quality outcomes and sustainable profits.
This article offers a comprehensive overview of the value chain in the Hair Restoration Market, mapping out the processes, players, and value-adding stages from start to finish.
1. Research & Development (R&D)
The foundation of any innovation in the Hair Restoration Market begins in R&D labs. This phase includes:
Clinical research on hair biology, including hormonal imbalances, DHT sensitivity, stem cell activity, and autoimmune causes of hair loss.
New treatment innovations, such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP), stem cell therapies, exosome solutions, and microneedling devices.
Formulation of products like serums, growth stimulants, DHT blockers, and therapeutic shampoos.
Development of robotic systems and AI algorithms for precise follicular unit extraction (FUE) and implantation.
Companies and universities collaborate through grants, patents, and licensing deals to push forward new technologies and techniques. R&D creates intellectual property that drives premium product offerings and market leadership.
2. Raw Material and Component Sourcing
Once R&D finalizes a treatment or device, the focus shifts to sourcing raw materials. This stage includes:
Medical-grade instruments and robotics used in surgeries.
Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) for topical and oral treatments.
Biological materials like PRP kits, growth factors, and regenerative components.
Packaging and labeling materials, especially for consumer-facing products.
Sourcing is critical to ensuring quality, safety, and regulatory compliance. Ethical sourcing and traceability have become priorities as consumers demand transparency.
3. Manufacturing and Quality Control
The production phase involves transforming raw materials into finished products. In this stage, manufacturers must:
Follow Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for medical and cosmetic products.
Implement quality control checkpoints at each phase—sterility, consistency, and potency are key parameters.
Adopt scalable automation to handle increasing demand for treatments and kits.
Collaborate with OEMs (original equipment manufacturers) for medical devices and robotic units.
Specialized manufacturing plants, often located in regulatory-compliant zones, ensure that products meet both domestic and international standards.
4. Distribution and Logistics
The products then move to distribution channels that connect manufacturers with clinics, medspas, hospitals, or directly to consumers. This stage includes:
Wholesale distributors supplying PRP kits, dermal tools, and drugs to clinics.
E-commerce platforms and retailers selling at-home treatment kits and supplements.
Medical tourism facilitators, especially in regions like Turkey, India, or Thailand, arranging logistics for foreign patients.
Efficient logistics systems with cold-chain transport, inventory tracking, and last-mile delivery enhance speed and reduce losses.
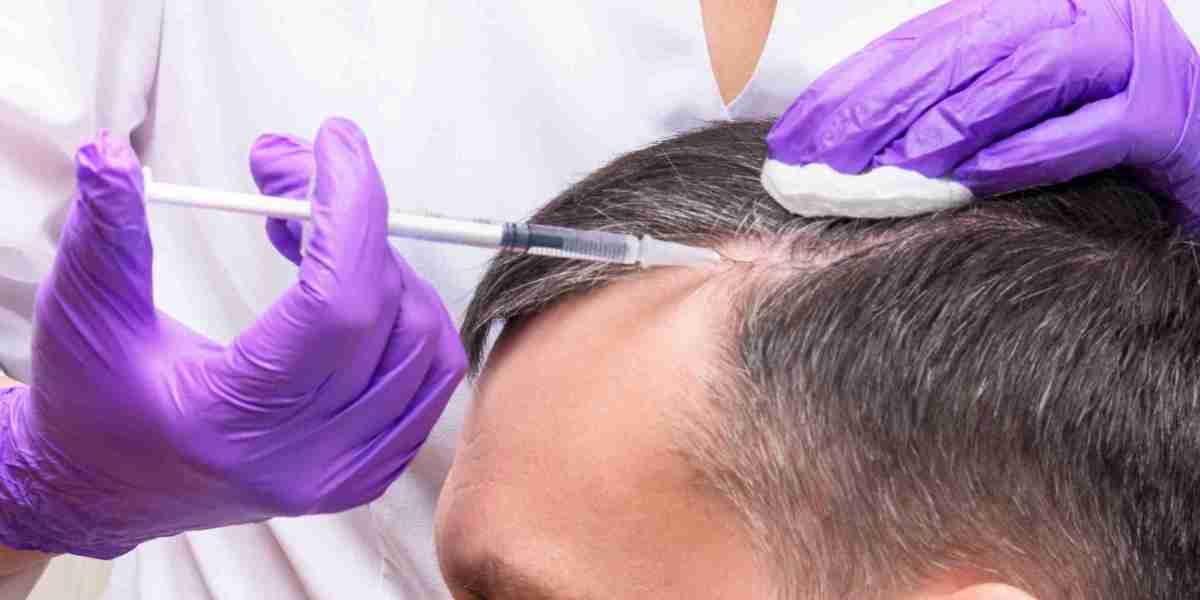
5. Clinics, Surgeons, and Service Providers
This is the most consumer-facing point in the value chain. Clinics and surgeons provide the treatments derived from earlier stages. Activities include:
Consultation and scalp diagnosis using AI imaging or trichoscopy.
Treatment delivery—surgical (FUE, FUT) or non-surgical (laser therapy, PRP, stem cell).
Patient education and customization, ensuring informed decision-making.
Post-treatment support, including follow-up visits, medication, and recovery guidance.
High-quality clinics invest in both skill and technology. Patient experience, ethical conduct, and aesthetic results determine the success at this stage.
6. Digital Marketing and Brand Communication
In the modern Hair Restoration Market, digital engagement is a crucial value-adding layer. Brands and clinics use:
SEO-optimized websites and informative blogs to educate potential patients.
Social media campaigns, influencer marketing, and testimonial videos to build trust.
CRM software for lead nurturing, appointment booking, and feedback collection.
Well-branded clinics and manufacturers create emotional resonance, helping patients feel understood and confident in their choices.
7. Consumer Use and Feedback
The end of the value chain lies in the hands of the consumers. Their experience, satisfaction, and feedback can loop back into the ecosystem:
Product reviews and ratings on marketplaces or social media.
Word-of-mouth recommendations to friends or family.
Repeat purchases of maintenance products or additional services.
Participation in loyalty programs or patient ambassador initiatives.
Patient feedback plays a vital role in refining services, product formulas, and even marketing language. In today’s market, every satisfied consumer can become a brand advocate.
8. Post-Treatment Care and Continuity
The final stage involves ongoing care to ensure long-term results and customer loyalty. It includes:
Routine follow-ups and scalp health monitoring
Sale of long-term use products, such as DHT blockers, regrowth serums, and multivitamins
Customized hair care regimes tailored to hair type, genetics, and lifestyle
Additional touch-up sessions or PRP boosters after initial treatment
This continuity phase allows businesses to extend the customer lifecycle, improving lifetime value and profitability.
Integrating the Value Chain: Strategic Advantages
Companies that effectively integrate all stages of the value chain gain several benefits:
Cost Efficiency: Streamlined sourcing, automation, and logistics reduce operational costs.
Speed to Market: Quick product development and delivery enable first-mover advantage.
Brand Control: Owning the full chain ensures quality and consistency.
Scalability: Better systems lead to faster geographic or demographic expansion.
Customer Retention: Continuity of care creates loyalty and referrals.
Vertical integration is increasingly popular among leading market players seeking tighter control and improved margins.
Conclusion
The Hair Restoration Market is more than just treatments—it is a comprehensive value chain linking scientific innovation to personal care. From R&D to post-treatment follow-up, each link adds distinct value, impacting cost, quality, accessibility, and customer satisfaction. For stakeholders in this industry, understanding and optimizing the value chain is essential for achieving sustainable growth and staying competitive in a rapidly evolving landscape.
![AFK Journey - Stratégies et Aventures [Guide]](https://pungi.b-cdn.net/upload/photos/2024/12/XNGEprxAO8dnVy1ysEAH_26_d2389e9429ac3181897c5693b2903e9a_image.png)


