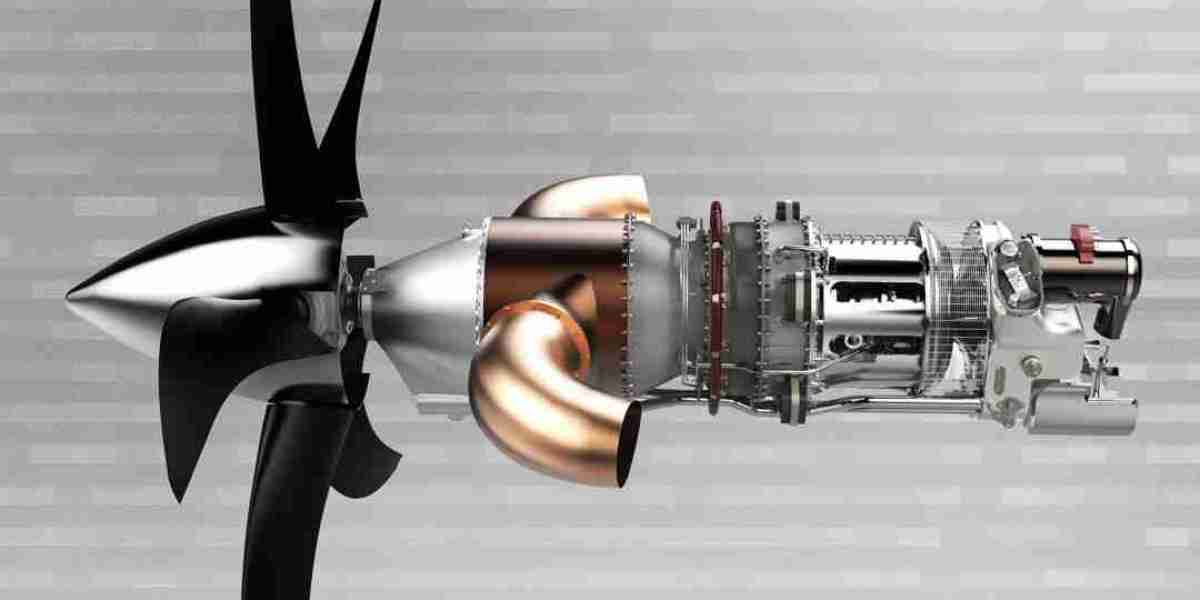
The turboprop engine market is witnessing a dynamic transformation, fueled by evolving regional aviation demands, technological advancements, and increasing focus on fuel-efficient propulsion systems. Turboprop engines, known for their superior performance in short-haul and regional flights, are regaining prominence as the aerospace industry emphasizes sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and connectivity to remote areas.
Market Overview
Turboprop engines are widely used in smaller commercial aircraft, military surveillance planes, cargo transporters, and agricultural aircraft due to their high efficiency at lower altitudes and speeds. The global turboprop engine market has shown stable growth in recent years, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 4% to 6% through the next decade.
Post-COVID-19, regional air travel has rebounded faster than long-haul international routes, boosting demand for aircraft powered by turboprop engines. Airlines and operators are investing in right-sized fleets to enhance connectivity between underserved cities, particularly in regions like Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
Key Market Drivers
1. Rising Regional Air Connectivity:
Government programs promoting regional connectivity, such as India’s UDAN scheme or Brazil’s regional aviation initiatives, have intensified demand for turboprop-powered aircraft. These aircraft are ideal for landing on short runways and unpaved airstrips, making them suitable for regional expansion.
2. Fuel Efficiency and Cost Optimization:
Turboprop engines offer better fuel efficiency than turbofan engines on shorter routes. As fuel costs remain a major concern for operators, the economical operation of turboprops makes them a practical solution, especially for low-margin regional services.
3. Environmental Concerns and Emission Norms:
With growing pressure on aviation to cut emissions, turboprops have a lower carbon footprint than jets over short distances. Manufacturers are actively developing next-generation engines with hybrid-electric capabilities and sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) compatibility.
4. Advancements in Engine Technology:
Recent innovations in materials, aerodynamics, and digital engine control systems are enhancing the reliability, safety, and lifecycle performance of turboprop engines. OEMs are also focused on reducing noise emissions, a key regulatory and passenger comfort issue.
Regional Analysis
North America:
The largest market for turboprop engines, driven by strong defense contracts, business aviation, and cargo transport. The U.S. remains a leader in engine manufacturing, with companies like Pratt & Whitney and GE Aviation at the forefront.
Europe:
Steady demand from commercial and military sectors is supported by European OEMs such as Rolls-Royce and Safran. Emphasis on green aviation is pushing research into hybrid-electric turboprop propulsion systems.
Asia-Pacific:
One of the fastest-growing markets due to rapid urbanization, tourism growth, and emerging regional air routes in countries like India, China, and Indonesia. Local players are also entering the manufacturing ecosystem, enhancing domestic supply chains.
Latin America and Africa:
These regions hold vast untapped potential for turboprop aircraft, especially for connecting rural and remote communities. However, limited infrastructure and funding pose challenges to rapid growth.
Competitive Landscape
The turboprop engine market is moderately consolidated, with a few major players controlling significant market share. Key companies include:
Pratt & Whitney – Known for the widely used PW100 series.
GE Aerospace – Offers advanced turboprop technologies, including in military platforms.
Rolls-Royce – Develops engines for both civilian and military turboprop applications.
Honeywell Aerospace – Supplies auxiliary and propulsion systems for light aircraft and drones.
Start-ups and smaller engine manufacturers are also entering niche segments, particularly in hybrid-electric propulsion, adding to market competition.
Challenges and Constraints
Despite positive trends, the market faces certain hurdles:
High Development Costs: R&D for cleaner and more efficient turboprop engines is capital-intensive.
Regulatory Approvals: Gaining certification for new technologies remains a lengthy and costly process.
OEM Dependency: Aircraft manufacturers often tie specific engines to their platforms, limiting competition.
Future Outlook
The turboprop engine market is expected to grow steadily with sustained regional travel demand, especially in emerging markets. Hybrid-electric and SAF-compatible engines are likely to become standard in the next generation of regional aircraft.
OEMs and suppliers focusing on innovation, cost efficiency, and sustainability will be best positioned to capture future opportunities. As global air travel patterns evolve, turboprop engines will continue to play a critical role in connecting smaller cities, driving inclusive growth in aviation.