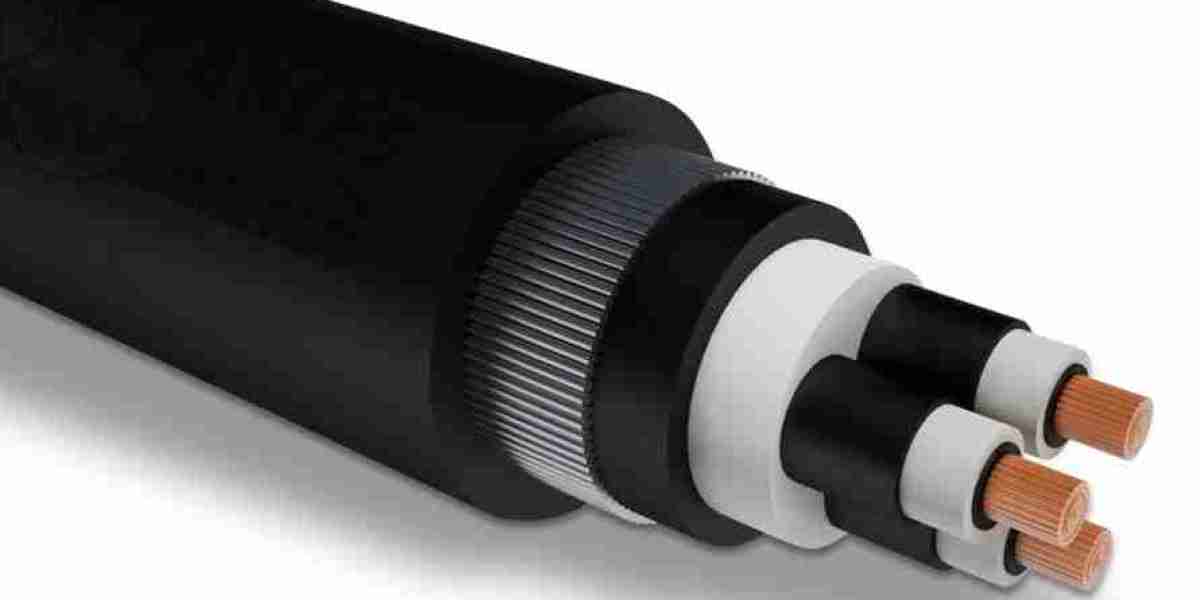
Cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) has evolved significantly since its introduction in the mid-20th century, emerging as a critical material in various industrial, commercial, and residential applications. The Cross-linked polyethylene market has witnessed strong growth over the last two decades, driven by its superior properties compared to traditional polyethylene, along with increasing demand from key sectors such as plumbing, heating, insulation, and infrastructure.
What is Cross-Linked Polyethylene?
Cross-linked polyethylene is a form of polyethylene with enhanced strength and durability, achieved through a cross-linking process that creates chemical bonds between polymer chains. This process modifies the structure of the polymer, making it more resistant to heat, pressure, chemicals, and environmental stress cracking. There are three primary methods of cross-linking polyethylene: peroxide (PEX-a), silane (PEX-b), and electron beam (PEX-c). Each method provides slightly different performance characteristics, which influence their applications and market demand.
Market Drivers
One of the primary drivers of PEX market growth is its widespread use in plumbing and heating systems. PEX tubing has become a preferred material for water supply lines and radiant floor heating systems due to its flexibility, ease of installation, resistance to scale and chlorine, and durability under extreme temperatures. Unlike metal pipes, PEX is not susceptible to corrosion or pitting, which enhances its lifespan and reduces maintenance costs.
The construction boom in emerging economies has further propelled demand for PEX. As urbanization accelerates, the need for reliable, efficient, and long-lasting piping systems increases. Governments and private developers are increasingly opting for materials that provide long-term cost savings and meet modern building codes—making PEX a favored choice.
In the industrial sector, PEX is also used for chemical transportation, cable insulation, and automotive components due to its resistance to heat and chemical degradation. As industries strive for higher performance materials, the appeal of PEX continues to rise.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in manufacturing processes and cross-linking technologies have been crucial in expanding the application scope of PEX. Innovations in extrusion techniques, automation, and quality control have improved production efficiency and material consistency. These improvements have enabled manufacturers to meet stringent regulatory standards in different regions, such as those related to drinking water safety and fire resistance.
The development of multilayer PEX pipes (incorporating aluminum or other materials) has also opened new opportunities. These pipes offer improved rigidity and oxygen barriers, which are particularly valuable in heating and cooling systems.
Regional Market Trends
North America and Europe represent mature markets for cross-linked polyethylene, largely driven by replacement demand and infrastructure modernization. In North America, particularly the United States, the PEX market has grown as the construction sector rebounds from previous slowdowns. The region’s focus on energy efficiency and sustainable building materials has supported the adoption of PEX-based heating systems and water distribution networks.
In Europe, environmental regulations and energy efficiency mandates have encouraged the use of advanced piping solutions like PEX. The region also places a strong emphasis on sustainable construction practices, contributing to steady demand.
Asia-Pacific, however, is expected to witness the fastest growth in the PEX market. Rapid urbanization, population growth, and increasing investments in housing and infrastructure development, especially in China and India, are creating a strong demand for advanced piping materials. The relatively lower labor costs and supportive government policies for manufacturing further enhance the region’s appeal as a production hub.
Challenges and Restraints
Despite its many advantages, the PEX market faces certain challenges. The initial cost of PEX materials can be higher than traditional options like PVC or copper, which may deter adoption in cost-sensitive markets. Additionally, PEX is not UV-resistant, limiting its use in outdoor applications unless adequately protected.
Environmental concerns around the recyclability of cross-linked polymers also present a long-term challenge. Unlike thermoplastics, cross-linked polymers cannot be melted and reprocessed, which makes recycling more difficult and less economically viable. However, research is ongoing to develop more sustainable production and disposal methods.
Future Outlook
The future of the PEX market looks promising, with continued innovation expected to address current limitations. Emerging applications in renewable energy systems (such as geothermal heating) and growing adoption in commercial buildings are likely to provide new avenues for expansion.
As global construction activity continues to rise and the need for resilient, efficient materials becomes more pronounced, cross-linked polyethylene is poised to maintain its position as a material of choice. Collaboration between manufacturers, researchers, and policymakers will be key to unlocking the next phase of growth—particularly in areas like sustainability, smart infrastructure, and material innovation.
In summary, the cross-linked polyethylene market is a dynamic and evolving sector with significant potential. Driven by its material advantages, rising global infrastructure demand, and ongoing technological progress, PEX is set to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of piping and insulation systems worldwide.