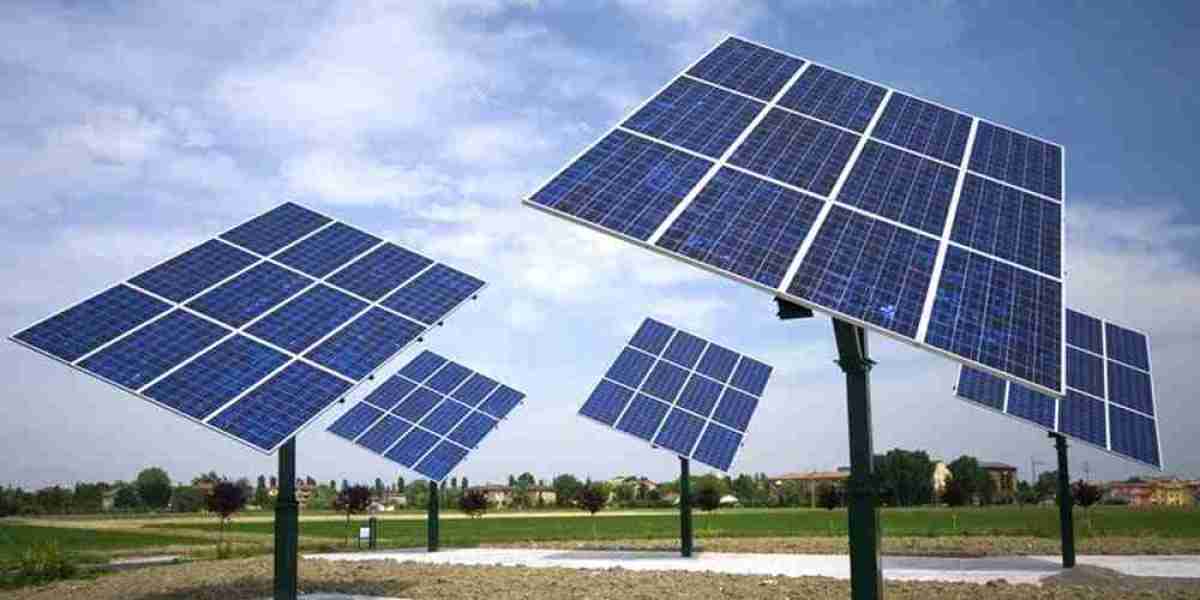
As the world increasingly embraces renewable energy, the solar industry has seen tremendous growth over the past decade. A key technological advancement contributing to this surge is the solar tracker — a device that orients solar panels toward the sun to maximize energy capture. While fixed-tilt systems are static, solar trackers dynamically adjust the position of the panels throughout the day. This adaptability significantly boosts energy output, often by 10–25%, depending on geographic location and technology.
The global solar tracker market has expanded rapidly, driven by a mix of environmental, economic, and technological forces. In this blog, we’ll explore the primary factors shaping the solar tracker market today.
1. Growing Demand for Renewable Energy
One of the biggest drivers of the solar tracker market is the global push toward clean and sustainable energy. Governments worldwide are implementing ambitious targets to reduce carbon emissions, and solar power is at the heart of most national renewable energy strategies. Solar trackers enhance the efficiency of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems, making them a more attractive option for utility-scale projects. As demand for high-yield solar farms grows, so too does the market for trackers.
2. Technological Advancements
Modern solar trackers are far more reliable and cost-effective than earlier versions. Innovations in smart sensors, control algorithms, IoT integration, and materials have improved durability and precision, allowing solar trackers to operate in diverse climates and terrains. These advancements have made dual-axis trackers more feasible, further boosting efficiency gains.
Moreover, solar trackers are now often integrated with machine learning and data analytics, which optimize performance based on weather conditions and historical patterns. These innovations are turning trackers into intelligent systems that adapt and evolve, creating new value for energy producers.
3. Declining Costs of Solar Technology
The cost of solar panels and associated technologies has plummeted over the last decade. As panels become cheaper, adding a tracker system to increase efficiency becomes more economically viable. The levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) — a key metric in energy production — decreases when more energy can be generated with the same panel area. This makes tracker-equipped systems increasingly cost-competitive with traditional energy sources.
4. Supportive Government Policies and Incentives
Governments across the globe are providing subsidies, tax incentives, and feed-in tariffs to encourage solar energy adoption. In many regions, utility-scale solar projects receive preferential treatment if they employ technologies that improve efficiency, such as solar trackers.
Policies like the Inflation Reduction Act in the U.S., the European Green Deal, and India’s national solar mission are directly contributing to the rising adoption of advanced solar infrastructure, including tracking systems.
5. Climate and Geographic Suitability
Solar trackers are most effective in regions with high solar irradiance and long daylight hours — typically sunbelt regions like the American Southwest, Southern Europe, the Middle East, and parts of Australia. In these areas, the added energy capture justifies the higher upfront cost of a tracker system. Consequently, geography significantly impacts market penetration.
However, cold climates and regions with frequent cloud cover or heavy snowfall may favor fixed-tilt systems, limiting the use of trackers. Manufacturers are now developing robust tracker systems that withstand extreme weather, opening up new geographic markets.
6. Land Use Optimization
Solar trackers can help reduce the land footprint of solar farms by improving energy output per panel. In land-constrained regions, this makes solar farms with trackers a more attractive solution. Additionally, innovations like bifacial panels paired with trackers enable even greater energy density by capturing reflected sunlight from the ground.
This focus on land-use efficiency is becoming increasingly important as solar deployment expands and competes for space with agriculture, urban development, and conservation efforts.
7. Competitive Industry Landscape
The solar tracker market is increasingly competitive, with major players like Nextracker, Array Technologies, Soltec, and Arctech Solar continually investing in R&D. This competition drives down prices while improving quality and features.
Additionally, mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships are reshaping the industry. Companies that can offer integrated, scalable solutions — combining tracking, mounting, and digital monitoring — are gaining a strong foothold.
Conclusion
The solar tracker market is at the intersection of sustainability, innovation, and economic viability. As the global energy transition accelerates, trackers will play a crucial role in maximizing the return on investment for solar installations. While factors such as climate, policy, and technology shape market dynamics, the overarching trend is clear: the demand for smart, efficient solar tracking solutions is poised for continued growth