The rise of contactless payments has transformed the way consumers make transactions, offering a faster, more convenient, and secure way to pay for goods and services. At the heart of this revolution are several key payment technologies that enable seamless transactions without the need for physical contact between the consumer and the payment terminal. These technologies — Near Field Communication (NFC), Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), QR codes, and emerging solutions — are driving growth in the contactless payment market, providing consumers with a range of payment options and contributing to a frictionless shopping experience.
In this article, we explore the key technologies that power the contactless payment market, how they work, and their roles in shaping the future of digital payments.
1. Near Field Communication (NFC): The Backbone of Contactless Payments
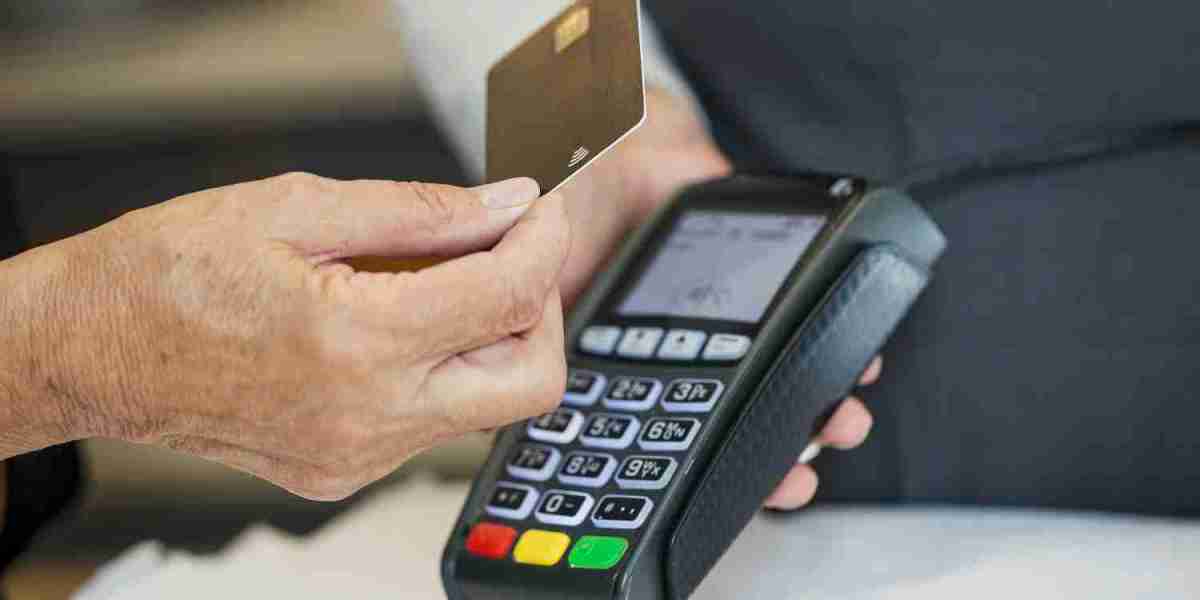
Near Field Communication (NFC) is perhaps the most widely known and adopted technology for contactless payments. NFC enables two devices to communicate wirelessly over short distances, typically a few centimeters, allowing for fast and secure transactions.
How NFC Works
NFC-based payments are typically made using contactless cards or smartphones equipped with NFC technology. When a customer makes a purchase, they simply tap their NFC-enabled device or card near an NFC terminal at the point of sale (POS). The communication happens almost instantly, with the customer receiving confirmation within seconds.
NFC payments are fast, secure, and widely accepted at most retailers, transport systems, and even online platforms. Major players in the mobile wallet space, such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay, use NFC to enable secure, one-tap payments from smartphones or wearables.
Key Benefits of NFC Payments
Speed: NFC payments are among the fastest contactless payment methods, enabling transactions to be completed in just a few seconds.
Security: NFC transactions use encryption and tokenization to protect sensitive data, ensuring that payment details are not transmitted in an easily accessible format.
Convenience: NFC enables one-tap payments, making the process easier and quicker for consumers and businesses alike.
2. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID): A Broader Application Beyond Payments
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is another technology that enables contactless payments, although it is often associated with inventory management and tracking. While RFID is similar to NFC in that it uses radio waves to communicate between devices, it operates over slightly longer distances.
How RFID Works in Payments
In an RFID-based contactless payment system, the payment card or device contains a microchip with an embedded RFID tag. When the user brings the RFID-enabled card or device near an RFID reader, the transaction is initiated without physical contact. While NFC payments typically work within a small range, RFID can function over a broader area, although it is still primarily used in contactless payment systems.
Many transit systems and contactless card-based payment solutions still rely on RFID for fast and efficient transactions.
Key Benefits of RFID Payments
Range: RFID tags can work over longer distances compared to NFC, which makes them useful in environments like public transportation systems and smart cards.
Durability: RFID tags are less sensitive to wear and tear than NFC tags, making them suitable for use in environments where cards may face rough conditions.
3. QR Codes: The Digital Alternative for Contactless Payments
QR codes (Quick Response codes) have emerged as a popular alternative to NFC and RFID in the contactless payment landscape. While QR codes do not rely on radio waves for communication, they offer a digital, contactless payment option that can be used by smartphones, tablets, and even feature phones that support QR scanning.
How QR Code Payments Work
QR code payments work by displaying a unique QR code on a merchant’s payment terminal or mobile app. The customer scans the code using their smartphone, which then triggers the payment process. The customer approves the payment through their mobile wallet or payment app, completing the transaction.
QR code-based payments are particularly popular in regions with lower smartphone penetration or where NFC terminals may be less widespread. They offer a universal payment solution that works across many types of mobile devices and does not require specialized hardware.
Key Benefits of QR Code Payments
Simplicity: QR codes can be easily generated and scanned using smartphones or mobile devices, making it a simple and low-cost option for both merchants and consumers.
No Need for Specialized Hardware: Unlike NFC or RFID, QR code payments don’t require merchants to invest in specialized contactless payment terminals. All that is needed is a smartphone with a camera and a QR code generation tool.
Global Reach: QR codes are widely used in Asia and are gaining traction globally due to their ability to operate on any mobile device.
4. Beyond NFC, RFID, and QR Codes: Emerging Payment Technologies
While NFC, RFID, and QR codes currently dominate the contactless payment market, new technologies are emerging to further enhance the way we make digital payments. These innovations aim to offer even faster, more secure, and more accessible options for consumers and businesses alike.
Biometric Payments
One of the most promising technologies on the horizon is biometric payments. Using fingerprint recognition, face recognition, or even iris scanning, biometric authentication can add an additional layer of security to contactless transactions. Some mobile wallets and payment platforms already use fingerprint authentication as an added security feature for verifying payments.
Voice-Activated Payments
With the rise of smart speakers and voice assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Siri, voice-activated payments are becoming a viable option for contactless transactions. Users can authorize payments or complete transactions simply by using voice commands, making it an incredibly convenient option for those already using voice-activated devices.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency
The integration of blockchain technology into digital payment systems is another disruptive trend in the contactless payment market. Cryptocurrency payments, particularly those using Bitcoin or Ethereum, offer secure, decentralized methods of payment that could transform how consumers pay online. While adoption is still limited, it is growing steadily, especially for cross-border transactions.
Wearable Payments
Another emerging trend is the use of wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers to make contactless payments. These devices, which are often equipped with NFC technology, allow users to make payments with just a tap, offering another level of convenience for those who prefer not to carry physical cards or smartphones.
Comparing Payment Technologies: NFC, RFID, QR Codes, and Beyond
| Technology | Range | Ease of Use | Security | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NFC | Short (~10 cm) | Very easy | High (Tokenization, Encryption) | Retail, Transit, Mobile Wallets |
| RFID | Medium to long | Easy | Medium (Encryption) | Public Transport, Smart Cards |
| QR Codes | Variable (depends on screen size) | Easy (scan-to-pay) | Medium (Depends on app security) | E-commerce, Retail, Food Delivery |
| Biometric Payments | Short (face/fingerprint recognition) | Easy (Requires biometric data) | Very High (Secure biometric data) | Banking, Online Shopping, Apps |
| Voice-Activated Payments | Short (voice command) | Very easy | High (Encryption + Authentication) | Smart Devices, Home Assistants |
| Blockchain/Crypto | Medium (varies by network) | Moderate (requires wallets) | Very High (Blockchain security) | Cross-border Payments, Digital Goods |
Conclusion
The contactless payment market is rapidly evolving, with several key technologies playing a significant role in enhancing the payment experience for consumers and merchants alike. NFC and RFID are leading the way, offering fast, secure, and convenient transactions for everyday purchases. Meanwhile, QR codes are democratizing contactless payments by making them accessible to a wider audience, especially in regions with less advanced payment infrastructure.