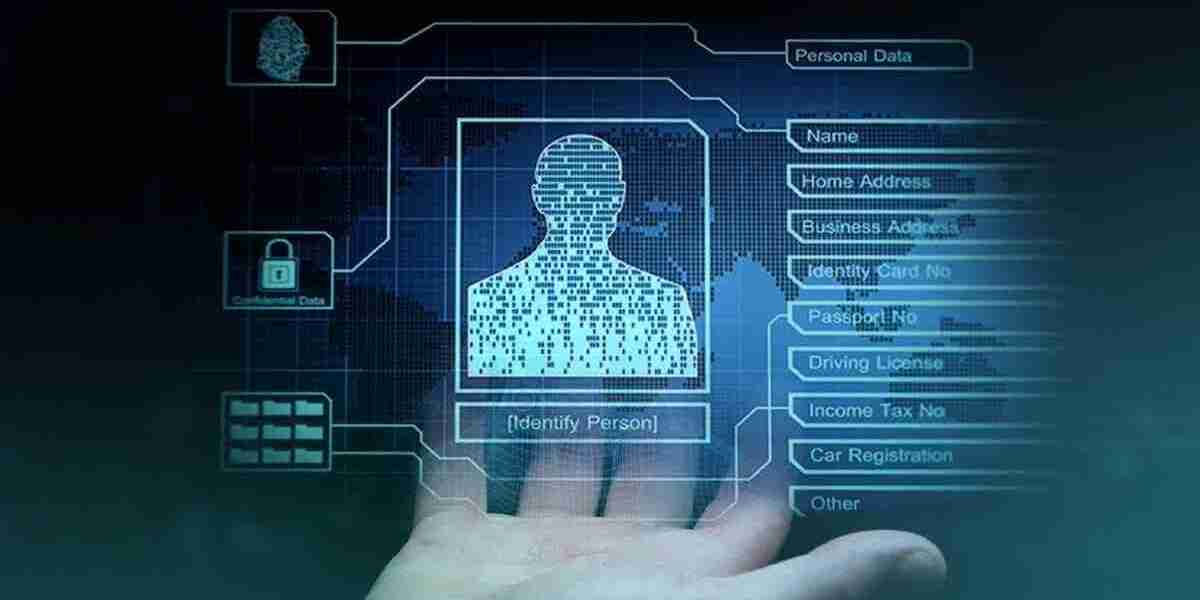
In today’s increasingly digital world, the digital identity solutions market is experiencing significant expansion. As businesses, governments, and consumers move towards secure and seamless online interactions, digital identity solutions have become a critical component of cybersecurity and user verification. However, privacy concerns and ethical considerations present major challenges to the widespread adoption and implementation of digital authentication solutions. This article explores these challenges and potential strategies to address them.
Privacy Concerns in Digital Identity Solutions
Data Security and Breach Risks
One of the most pressing concerns in digital identity management is the risk of data breaches. Cybercriminals target identity databases to gain unauthorized access to sensitive personal information, leading to financial fraud and identity theft. Companies must invest in advanced encryption, decentralized identity models, and continuous monitoring to enhance security.
User Consent and Data Ownership
Many digital identity systems collect extensive personal information, raising concerns about user consent and data ownership. Consumers are demanding greater control over their personal data, prompting the need for transparent data collection policies and user-centric identity frameworks, such as self-sovereign identity (SSI) models.
Government Surveillance and Privacy Infringement
Government-led digital identity programs, while improving service efficiency, raise concerns about mass surveillance and potential misuse of personal data. Ensuring strong data protection laws and ethical guidelines for digital ID programs is essential to prevent privacy violations.
Ethical Considerations in Digital Authentication
Bias in Biometric and AI-Based Authentication
AI-driven authentication systems and biometric technologies have been criticized for biases in recognizing individuals based on race, gender, or age. Ensuring fair and inclusive digital identity solutions requires training AI models with diverse datasets and implementing bias-mitigation strategies.
Ethical Use of Biometric Data
Biometric authentication, including fingerprint and facial recognition, is increasingly used for identity verification. However, concerns about the ethical collection, storage, and use of biometric data persist. Organizations must establish clear policies on biometric data retention and implement stringent access controls to prevent misuse.
Digital Exclusion and Accessibility
Not all individuals have equal access to digital identity solutions, leading to digital exclusion, particularly in underserved communities. Ensuring that digital identity systems are accessible, inclusive, and compatible with various devices and connectivity conditions is crucial to bridging the digital divide.
Strategies for Addressing Privacy and Ethical Challenges
Implementing Privacy-by-Design Principles
Organizations should integrate privacy-by-design principles into digital identity solutions, ensuring that security and user privacy are considered from the development stage. Features like minimal data collection, encryption, and decentralized identity models can enhance privacy protection.
Strengthening Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to global privacy regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and eIDAS, helps companies align with legal and ethical standards for digital identity management. Organizations must stay updated on evolving compliance requirements and implement robust data protection policies.
Enhancing Transparency and User Control
Providing users with greater transparency regarding how their data is collected, stored, and used can build trust in digital identity solutions. Implementing consent-based identity management and offering users the ability to revoke access to their data enhances control and security.
Future Outlook: Balancing Innovation with Privacy and Ethics
As digital identity solutions evolve, balancing innovation with privacy and ethical considerations will be crucial for sustainable growth. Businesses, regulators, and technology providers must collaborate to create secure, ethical, and user-centric identity management systems. By addressing privacy concerns and promoting ethical digital authentication practices, the digital identity solutions market can ensure trust, security, and inclusivity in the digital age.
In conclusion, while digital identity solutions offer immense benefits in enhancing security and authentication, they also present challenges related to privacy, ethics, and digital inclusivity. Addressing these concerns through privacy-focused frameworks, ethical AI development, and strong regulatory compliance will be key to shaping a secure and trustworthy digital identity ecosystem.