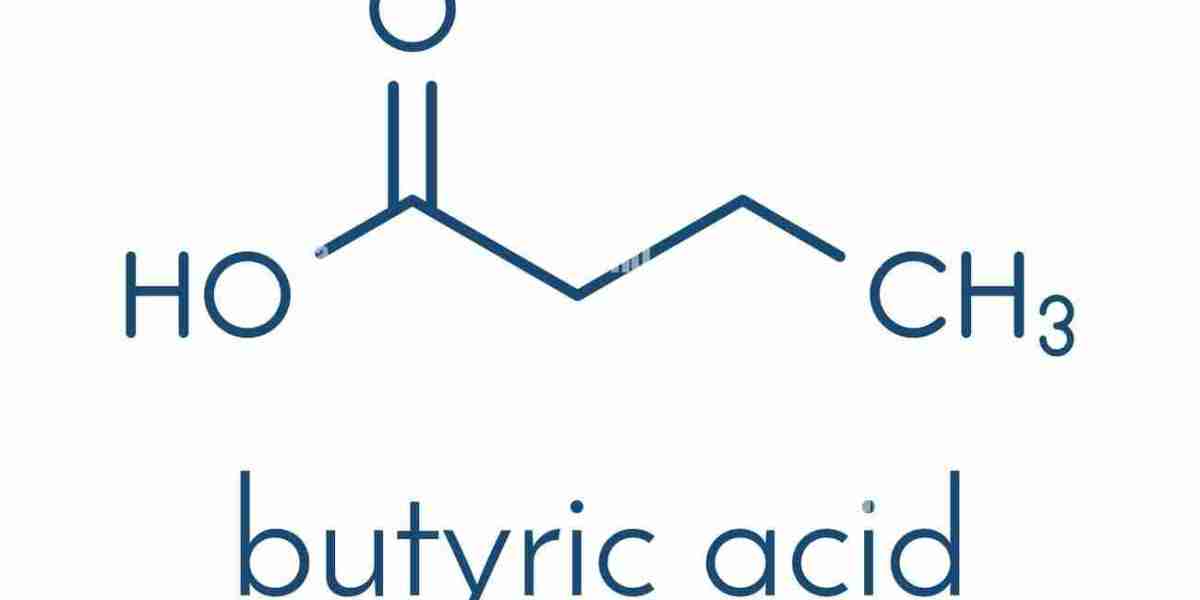
The butyric acid market is a dynamic segment within the global chemical industry, experiencing steady growth due to its applications in food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, animal feed, and chemical intermediates. However, despite its promising potential, the market faces several restraints that hinder its expansion. These challenges include regulatory hurdles, environmental concerns, fluctuating raw material prices, competition from substitutes, and technological constraints. Understanding these barriers is crucial for industry players to devise strategic approaches to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities.
1. Stringent Regulatory Frameworks
One of the primary restraints in the butyric acid market is the stringent regulatory landscape. Various government agencies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), impose strict guidelines on the production, handling, and application of butyric acid, particularly in the food and pharmaceutical sectors.
For instance, butyric acid used as a food additive or animal feed supplement must meet rigorous safety standards, which often require extensive testing and compliance documentation. Similarly, its use in pharmaceuticals is subject to regulatory approvals that can be time-consuming and costly. Manufacturers need to adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other safety protocols, which can increase production costs and limit market entry for smaller firms.
2. Environmental Concerns and Disposal Challenges
Environmental issues present another significant restraint for the butyric acid market. Although butyric acid is a naturally occurring compound, its industrial production involves chemical synthesis that can result in harmful by-products and emissions. The disposal of waste generated during production must be managed in compliance with environmental protection laws, which adds to operational expenses.
Additionally, butyric acid has a strong, unpleasant odor, which poses challenges for its handling, storage, and transportation. Facilities dealing with large-scale production must invest in odor control systems and proper ventilation, further increasing operational costs. Concerns about air pollution and potential health hazards associated with prolonged exposure to butyric acid vapors also lead to restrictions on its industrial usage, particularly in regions with strict environmental laws.
3. Fluctuations in Raw Material Prices
Raw material price volatility is another major restraint in the butyric acid market. The primary sources for manufacturing butyric acid include petroleum-based chemicals and biological fermentation of biomass. Crude oil price fluctuations significantly impact the cost of petrochemical-derived butyric acid, making pricing strategies unpredictable for manufacturers.
Additionally, bio-based butyric acid production depends on feedstocks like corn, sugarcane, and molasses, which are subject to seasonal variations, climate change, and global supply chain disruptions. Factors such as droughts, changes in agricultural policies, and increasing competition for biomass feedstocks further complicate cost predictability. As a result, manufacturers must constantly adapt to changing market conditions, which can deter investment in large-scale production facilities.
4. Competition from Substitute Products
The butyric acid market faces stiff competition from alternative products that can serve similar functions across various industries. In the animal feed sector, for instance, other organic acids like propionic acid, acetic acid, and lactic acid are commonly used as feed additives to improve gut health in livestock. These alternatives are often more cost-effective or widely available, making them attractive substitutes for butyric acid.
Similarly, in the chemical industry, synthetic esters and fatty acids can replace butyric acid in the production of flavors, perfumes, and pharmaceuticals. The availability of these substitutes reduces the overall demand for butyric acid, especially in price-sensitive markets. Manufacturers must continuously innovate and enhance the competitive advantages of butyric acid to maintain its market share against these alternatives.
5. High Production and Operational Costs
The production of butyric acid, especially bio-based variants, involves advanced fermentation technologies that require significant capital investment. Establishing fermentation-based production facilities involves high initial costs, complex bioprocess engineering, and continuous research and development (R&D) efforts.
Moreover, maintaining fermentation efficiency and ensuring consistent product quality can be challenging due to variations in microbial performance and substrate availability. Unlike chemical synthesis, which offers relatively higher production efficiency, fermentation-based production is more susceptible to contamination and yield fluctuations. These technical challenges contribute to higher production costs, which can make bio-based butyric acid less competitive compared to its synthetic counterpart.
6. Limited Awareness and Adoption in Emerging Markets
Although the demand for butyric acid is rising in developed markets, awareness and adoption remain limited in emerging economies. Many businesses and consumers in developing regions lack familiarity with the benefits of butyric acid, particularly in animal feed and pharmaceutical applications. Additionally, price sensitivity in these markets makes it difficult for premium-priced butyric acid products to gain widespread acceptance.
Furthermore, the infrastructure required for efficient production, transportation, and storage of butyric acid is often underdeveloped in emerging economies. A lack of research institutions and industry collaboration in these regions further slows down market expansion. To overcome these challenges, companies need to focus on education, market penetration strategies, and local partnerships.
7. Supply Chain Disruptions
Global supply chain disruptions pose another significant restraint on the butyric acid market. Factors such as trade restrictions, geopolitical tensions, labor shortages, and logistical challenges can lead to delays in raw material procurement and product distribution. The COVID-19 pandemic, for example, highlighted the vulnerabilities of global supply chains, causing price spikes and production delays across various chemical sectors.
The transportation of butyric acid requires specialized handling due to its corrosive nature and odor issues. Any disruptions in supply chains can lead to increased lead times and operational inefficiencies for manufacturers and end-users. Companies must invest in resilient supply chain strategies, including local sourcing and diversification of raw material suppliers, to mitigate these risks.
Conclusion
Despite its growing demand in various industries, the butyric acid market faces several constraints that limit its expansion. Stringent regulations, environmental concerns, raw material price volatility, competition from substitutes, high production costs, limited awareness in emerging markets, and supply chain disruptions are among the key challenges. Addressing these barriers requires strategic investments in research, sustainable production methods, regulatory compliance, and market awareness initiatives. By overcoming these obstacles, industry players can unlock new growth opportunities and strengthen the market position of butyric acid in the global chemical landscape.