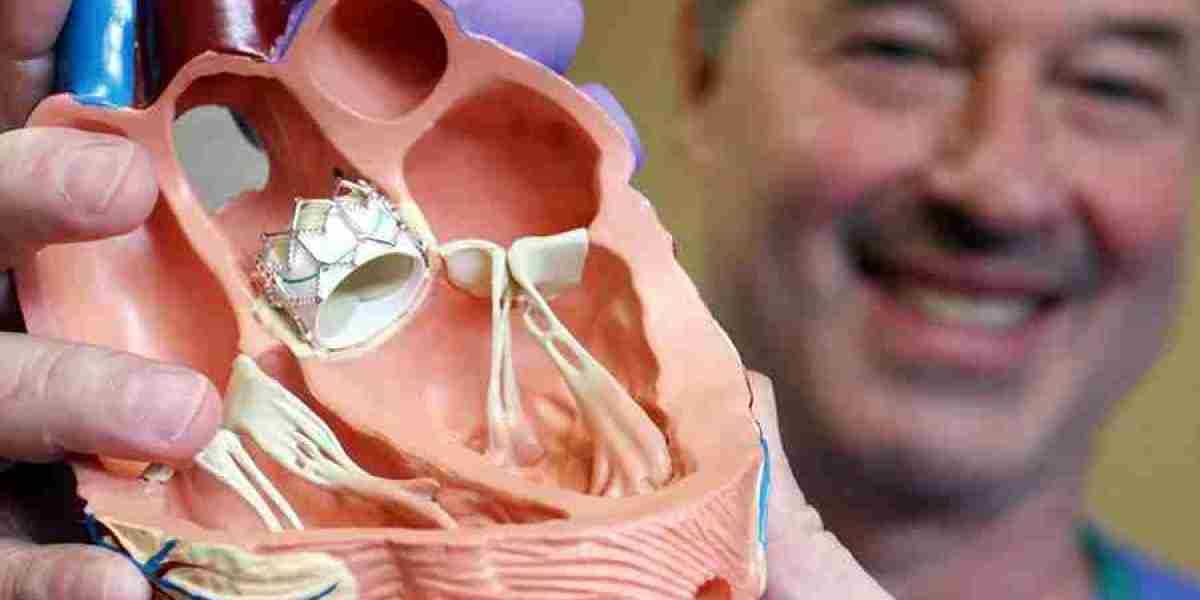
The prosthetic heart valves market has witnessed remarkable growth in recent years, driven by the rising prevalence of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), advancements in transcatheter valve technologies, and increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures. However, despite this positive momentum, several challenges and market restraints hinder its full potential. From regulatory hurdles to high procedural costs, these barriers create friction for manufacturers, healthcare providers, and patients alike. Understanding these constraints is essential for market players seeking to navigate the complexities of this evolving industry.
1. High Cost of Valve Replacement Procedures
One of the most significant restraints in the prosthetic heart valves market is the high cost associated with valve replacement procedures, particularly transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). While TAVR has transformed the treatment landscape for patients with aortic stenosis, it comes with a hefty price tag.
Cost Breakdown:
TAVR Procedure: On average, TAVR costs between $30,000 and $70,000 per patient in the United States, making it financially inaccessible for many patients, especially in lower-income regions.
Mechanical and Biological Valves: Surgical valve replacement procedures, while less expensive than TAVR, still range between $10,000 and $25,000, excluding hospitalization and aftercare costs.
Impact on Market Growth:
In developing countries, the high cost limits patient access to life-saving procedures.
Even in developed regions, reimbursement challenges prevent certain patients from affording prosthetic heart valves, restricting market penetration.
2. Durability and Lifespan Limitations
While prosthetic heart valves significantly improve patient outcomes, their limited durability presents a major challenge, particularly for younger patients.
Durability Issues by Valve Type:
Biological (Tissue) Valves: Despite being less thrombogenic, biological valves have a shorter lifespan of around 10–15 years. Younger patients who receive tissue valves often require repeat surgeries, which adds to healthcare costs and procedural risks.
Mechanical Valves: While these valves are more durable, they require lifelong anticoagulation therapy to prevent blood clots. This carries the risk of bleeding complications, creating a trade-off between longevity and safety.
Market Implications:
The need for reoperation due to valve degeneration creates additional expenses and patient risks.
Limited durability deters some healthcare providers from recommending certain prosthetic valves, slowing market adoption.
3. Regulatory and Approval Complexities
The prosthetic heart valve market is heavily regulated due to the critical nature of these medical devices. Obtaining regulatory approvals from bodies such as the U.S. FDA, European Medicines Agency (EMA), and other health authorities is a lengthy and expensive process.
Challenges in Regulatory Approval:
Stringent clinical trial requirements: Manufacturers must conduct large-scale clinical trials to demonstrate safety, efficacy, and durability. This increases time to market.
Changing regulations: Regulatory frameworks often evolve, requiring manufacturers to adapt and comply with new standards, which adds to production costs and delays.
Post-market surveillance: Even after approval, prosthetic valves undergo continuous monitoring for adverse events, further complicating market entry.
Impact on Market Dynamics:
Slower product launches due to prolonged approval processes.
Increased costs for manufacturers to meet regulatory standards.
Limited access to newer technologies in regions with stricter regulatory environments.
4. Risk of Complications and Long-Term Side Effects
Despite technological advancements, prosthetic heart valve implantation still carries risks of post-operative complications. This remains a restraint, especially for patients who might be hesitant to undergo the procedure.
Common Complications:
Thrombosis and Stroke: Mechanical valves increase the risk of blood clots, necessitating anticoagulation therapy, which can lead to bleeding complications.
Infections (Endocarditis): Patients with prosthetic valves face a lifelong risk of infective endocarditis, a rare but life-threatening complication.
Valve Leakage and Malfunction: Valve regurgitation or paravalvular leakage can occur, requiring reintervention or surgical correction.
Market Impact:
Patient reluctance: The potential for complications deters some patients from opting for prosthetic valve replacement.
Physician hesitancy: Surgeons may be cautious in recommending valve replacement, especially for younger or low-risk patients, due to the risks of reoperation and long-term complications.
5. Lack of Skilled Healthcare Professionals
The successful implantation of prosthetic heart valves, especially in TAVR procedures, requires highly trained interventional cardiologists and cardiovascular surgeons. However, workforce shortages in many regions limit the availability of these life-saving treatments.
Challenges in Healthcare Workforce:
Limited TAVR expertise: TAVR, being a newer procedure, requires specialized training. Many regions, particularly in emerging markets, lack sufficient skilled professionals.
Training and certification costs: Surgeons need extensive training and certification, which can be costly and time-consuming, restricting the expansion of TAVR programs.
Hospital capacity constraints: In regions with fewer specialized centers, patient access to prosthetic valve procedures is reduced.
Consequences for the Market:
Slower procedure adoption due to workforce limitations.
Uneven geographical availability, with rural or less-developed areas having restricted access to valve replacement therapies.
6. Limited Adoption in Emerging Markets
While North America and Europe dominate the prosthetic heart valve market, emerging markets face significant barriers to entry.
Key Challenges:
Lack of awareness: In many developing regions, patients and healthcare providers have limited knowledge about prosthetic valve treatments.
Weak healthcare infrastructure: Limited access to advanced healthcare facilities and diagnostic capabilities restricts the adoption of prosthetic valves.
Affordability issues: Even with growing healthcare investments, the high costs of procedures remain a significant hurdle for low- and middle-income populations.
Impact on Market Expansion:
Slow penetration of prosthetic valve technologies in emerging regions.
Revenue concentration in high-income countries, limiting global market potential.
Conclusion
While the prosthetic heart valves market offers significant growth potential, several constraints limit its full expansion. High procedural costs, durability challenges, regulatory complexities, and the risk of complications continue to hinder widespread adoption. Moreover, the lack of skilled healthcare professionals and limited accessibility in emerging markets further restricts the market’s reach.
For industry players, addressing these restraints will be key to unlocking new growth opportunities. Investments in cost-effective technologies, durability improvements, and workforce training will be essential for overcoming current market barriers. As the market evolves, overcoming these challenges will be critical to ensuring broader access to life-saving prosthetic heart valve procedures worldwide.