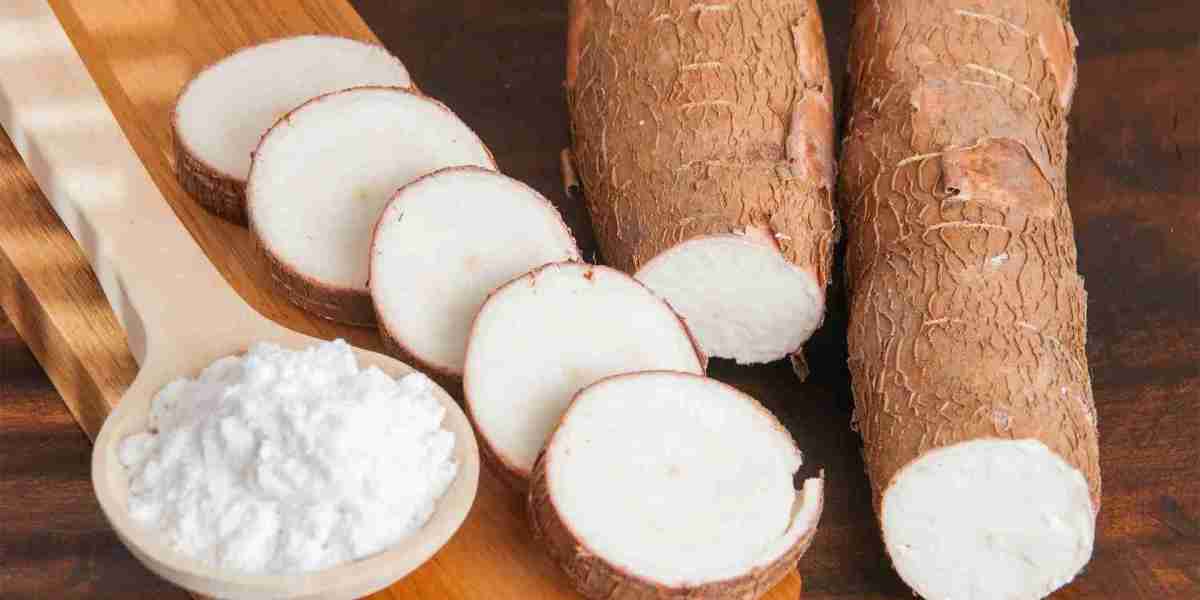
The native starch market faces numerous challenges, limiting its growth and development across different sectors. Native starch, derived from sources like corn, wheat, and cassava, is widely used in food and beverage, paper, textiles, and pharmaceutical industries. However, despite its versatility, several factors hinder its market expansion, affecting manufacturers and consumers alike.
Regulatory Constraints and Quality Standards
Stringent regulations concerning food safety and quality are a significant restraint in the native starch industry. Regulatory bodies enforce strict guidelines for the use of starch in food products, creating challenges for producers to meet compliance standards. Additionally, the absence of uniform global standards adds further complexity, leading to additional testing and certification expenses.
Price Volatility and Raw Material Dependency
The market is heavily dependent on agricultural commodities, making it vulnerable to price fluctuations and supply chain disruptions. Factors like unfavorable weather conditions, pest infestations, and geopolitical tensions can impact raw material availability, causing unpredictable price swings. Manufacturers often face increased production costs, reducing profit margins and limiting market growth.
Competition from Modified Starch Alternatives
The growing preference for modified starches, which offer enhanced properties such as improved stability and functionality, presents a major challenge for native starch producers. Modified starches are preferred in applications where native starch may fall short, especially in processed foods and industrial applications. The demand for tailored starch solutions further intensifies the competition.
Limited Functional Capabilities
Native starch has inherent limitations in terms of stability, resistance to high temperatures, and mechanical stress. Its inability to perform efficiently in certain industrial applications restricts its adoption. Industries requiring longer shelf-life products or high-temperature processing often opt for modified starch or synthetic alternatives, further constraining the market's growth potential.
Sustainability and Environmental Concerns
While native starch is biodegradable and eco-friendly, its production processes can still have environmental impacts. Excessive water usage, soil degradation, and chemical fertilizers used in starch cultivation raise sustainability concerns. Additionally, waste generation during starch extraction and processing contributes to environmental challenges, pushing industries to explore more sustainable alternatives.
Logistics and Supply Chain Challenges
Transporting raw materials and finished starch products across international borders presents logistical challenges. Delays in transportation, inadequate storage facilities, and inconsistent supply chain management impact the timely availability of native starch. These inefficiencies can lead to increased costs and reduced market competitiveness.
Technological Advancements in Alternatives
Innovations in biotechnology and material science have led to the development of advanced starch alternatives. Synthetic starches and bio-based polymers offer superior performance characteristics, reducing the reliance on native starch. The growing emphasis on research and development in alternative products adds further pressure on the native starch industry.
Conclusion
While the native starch market remains an essential component of various industries, numerous restraints continue to challenge its growth. Addressing regulatory compliance, reducing raw material dependency, and enhancing product functionality through innovation can help mitigate these challenges. Moreover, adopting sustainable practices and improving supply chain efficiencies can further strengthen the market's resilience in the face of these constraints.