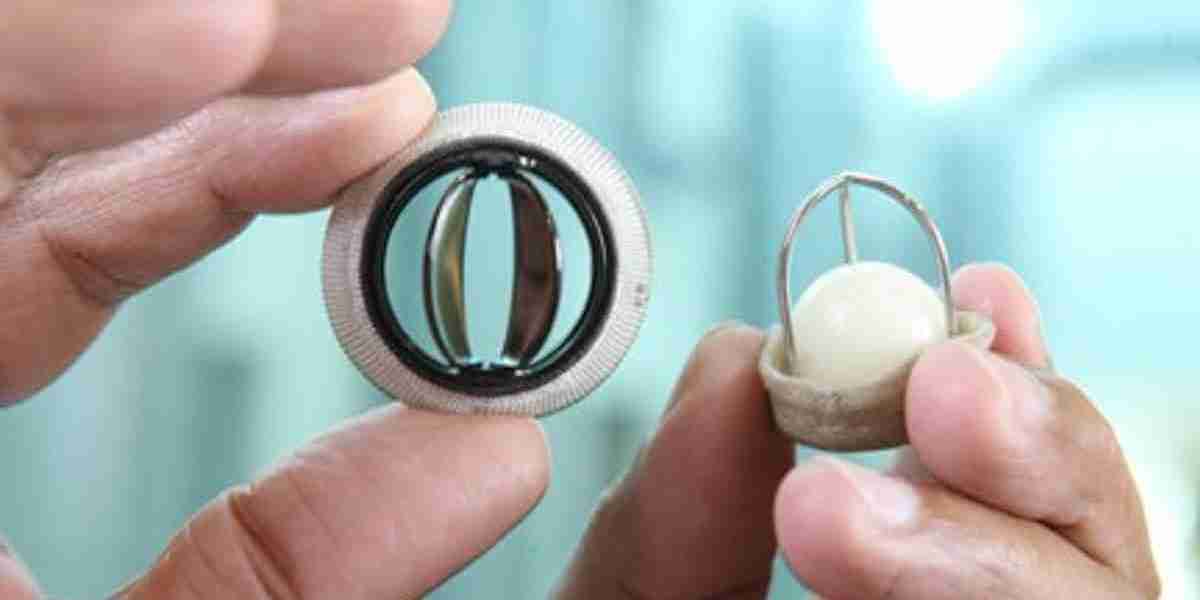
Prosthetic heart valves market has witnessed significant growth over the past decade, driven by advancements in medical technology, an aging population, and an increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases. However, beyond these clinical factors, the economic landscape plays a crucial role in shaping the global demand for prosthetic heart valves. From healthcare expenditures and reimbursement policies to regional disparities in income and access to healthcare services, economic factors are key determinants in how and where prosthetic heart valves are adopted. This article delves into the various economic factors influencing the demand for prosthetic heart valves worldwide.
Healthcare Expenditures and Government Funding:
Healthcare expenditure is a fundamental factor driving the demand for prosthetic heart valves across different regions. Countries with higher healthcare spending typically have greater access to advanced medical technologies, including heart valve replacements. In regions like North America and Western Europe, where healthcare spending is relatively high, hospitals and medical facilities can invest in cutting-edge treatments like Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR). This minimally invasive procedure is increasingly preferred over traditional open-heart surgery due to its shorter recovery times and lower complication rates.
In contrast, developing countries with lower healthcare budgets may struggle to adopt these advanced procedures on a wide scale. For example, in parts of Asia-Pacific and Latin America, healthcare systems may still rely on more traditional surgical techniques, as the cost of implementing newer technologies like TAVR can be prohibitive. Government funding plays a crucial role in determining how well healthcare systems can absorb the costs of new procedures and devices. Countries with strong government support for healthcare tend to have more widespread access to prosthetic heart valves, regardless of income disparities among patients.
Reimbursement Policies and Insurance Coverage:
Reimbursement policies are another economic factor that heavily influences the global demand for prosthetic heart valves. In countries with comprehensive insurance coverage and favorable reimbursement structures, patients are more likely to undergo valve replacement procedures, as the financial burden is alleviated. In the United States, for example, Medicare and private insurers provide extensive coverage for prosthetic heart valve procedures, particularly for high-risk patients who may benefit from TAVR. This has spurred significant growth in the U.S. market, with more hospitals offering the procedure to eligible patients.
Similarly, many European countries with universal healthcare systems provide full or partial reimbursement for heart valve replacements, making these life-saving procedures accessible to a broader population. However, not all regions have the same level of reimbursement support. In developing countries, where insurance coverage may be limited, patients often face higher out-of-pocket costs for heart valve procedures, leading to lower demand for advanced treatments like TAVR. The disparity in reimbursement policies creates an uneven playing field, with wealthier nations benefiting from higher adoption rates of prosthetic heart valves compared to lower-income countries.
Income Levels and Affordability:
Income levels directly impact a patient’s ability to access advanced medical treatments. In high-income regions, such as North America and parts of Europe, patients are more likely to afford the costs associated with prosthetic heart valve procedures, particularly in cases where insurance coverage is limited or where certain procedures are not fully reimbursed. The ability to pay for treatments out-of-pocket can drive demand for high-cost procedures like TAVR, even in the absence of comprehensive insurance coverage.
Conversely, in low- and middle-income countries, affordability remains a major barrier to accessing advanced heart valve treatments. The high cost of prosthetic heart valves, particularly newer bioprosthetic valves, makes these procedures inaccessible for a significant portion of the population. In countries like India, Brazil, and China, the demand for lower-cost alternatives, such as mechanical valves or traditional open-heart surgery, remains high due to affordability concerns. As healthcare systems in these regions continue to evolve, there is potential for increased demand for prosthetic heart valves, but affordability will continue to play a crucial role in determining access to advanced procedures.
Regional Disparities in Access to Healthcare:
Economic factors also contribute to regional disparities in access to healthcare, which, in turn, affects the demand for prosthetic heart valves. In regions with well-developed healthcare infrastructures, such as Western Europe, North America, and parts of Asia-Pacific (e.g., Japan and South Korea), patients have greater access to specialized cardiovascular care, including heart valve replacement procedures. These regions typically have more hospitals equipped to perform advanced procedures like TAVR, contributing to higher demand for prosthetic heart valves.
In contrast, regions with less developed healthcare systems, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia, face significant barriers to accessing cardiovascular care. A lack of specialized facilities, trained medical professionals, and advanced medical devices limits the availability of prosthetic heart valve procedures. As a result, the demand for heart valve replacements in these regions remains lower, even as the prevalence of cardiovascular diseases increases.
Economic Growth and Market Expansion:
Economic growth in emerging markets presents a significant opportunity for the expansion of the prosthetic heart valves market. Countries such as China, India, and Brazil are experiencing rapid economic development, leading to increased healthcare spending and improved access to medical treatments. As these countries invest more in healthcare infrastructure and insurance coverage expands, the demand for advanced medical devices, including prosthetic heart valves, is expected to grow.
However, market expansion in these regions will depend on several factors, including the ability to make advanced procedures like TAVR more affordable and accessible to a broader population. The increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases in emerging markets, coupled with economic growth, suggests that these regions could become key drivers of future demand for prosthetic heart valves.
Conclusion:
The prosthetic heart valves market is shaped by a range of economic factors, including healthcare expenditures, reimbursement policies, income levels, and regional disparities in access to healthcare. While high-income regions with well-developed healthcare systems continue to lead the market in terms of adoption of advanced procedures like TAVR, emerging markets present significant growth opportunities as they improve their healthcare infrastructure and expand access to medical treatments. Moving forward, addressing economic barriers such as affordability and insurance coverage will be crucial to ensuring broader access to life-saving prosthetic heart valve procedures across all regions.