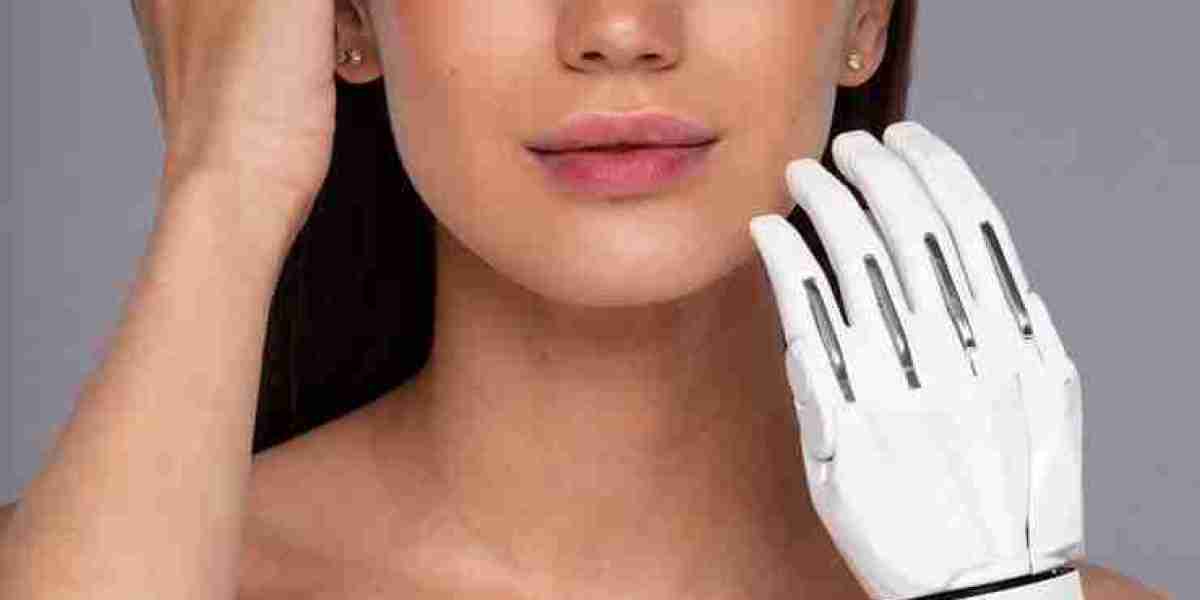
The electronic skin market is a rapidly growing segment in the smart healthcare, robotics, and wearable technology industry. With innovations in flexible sensors, self-healing materials, and AI-powered applications, electronic skin has the potential to revolutionize various sectors. However, despite its promising future, the market faces significant threats that could hinder its widespread adoption and commercial success.
1. High Research and Development Costs
One of the most significant challenges in the electronic skin market is the high cost of research and development (R&D). Developing advanced e-skin with self-healing properties, enhanced sensitivity, and integration with AI requires extensive investment in materials, sensors, and biocompatibility testing. Startups and small-scale enterprises often struggle to compete due to limited financial resources, making it difficult to bring their innovations to market.
Moreover, the need for sophisticated infrastructure and specialized expertise further increases the overall cost. If the production costs remain high, the affordability and accessibility of electronic skin products will be restricted, limiting their adoption across various industries.
2. Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
Electronic skin technology, particularly in healthcare applications, must comply with strict regulations and safety standards before it can be used in medical devices. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) impose rigorous testing and approval processes to ensure safety and effectiveness.
These compliance requirements can lead to long delays in product launches, increased expenses for companies, and potential legal hurdles if a product fails to meet regulatory standards. Additionally, varying global regulations make it difficult for manufacturers to enter multiple international markets seamlessly.
3. Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Risks
As electronic skin becomes increasingly integrated with AI, IoT (Internet of Things), and cloud-based health monitoring systems, cybersecurity risks are growing concerns. The data collected by electronic skin devices, including vital signs and health conditions, is highly sensitive. If not adequately protected, this data could be vulnerable to cyberattacks and unauthorized access.
A single breach in the system could compromise personal health data, leading to privacy violations and legal repercussions. Ensuring robust encryption, secure cloud storage, and compliance with data protection laws such as GDPR and HIPAA is essential for maintaining consumer trust in the technology.
4. Material Limitations and Durability Issues
Although research in electronic skin materials has advanced significantly, durability remains a major concern. The material must be flexible, stretchable, self-healing, and biocompatible, all while maintaining sensor efficiency and conductivity over time.
Currently, many e-skin products suffer from short lifespans due to material degradation, environmental exposure, or mechanical stress. For electronic skin to become commercially viable in industries such as prosthetics, robotics, and medical monitoring, it must withstand daily wear and tear while maintaining high performance.
5. Competitive Market and Intellectual Property Issues
The electronic skin industry is highly competitive, with leading technology companies, academic institutions, and startups racing to develop and commercialize new solutions. This competition often leads to intellectual property (IP) disputes over patents, proprietary sensor technologies, and innovative material compositions.
Large corporations with extensive financial and legal resources can dominate the market by acquiring patents and blocking smaller competitors from entering. This situation could stifle innovation and limit the diversity of electronic skin products available to consumers.
Furthermore, counterfeit or low-quality versions of electronic skin may enter the market, leading to safety risks and diminishing consumer confidence in legitimate products.
Conclusion
While the electronic skin market holds immense potential for transforming industries, several threats hinder its progress. High development costs, regulatory challenges, cybersecurity risks, material limitations, and intense competition create significant roadblocks. To overcome these challenges, companies must focus on cost-effective production methods, regulatory collaboration, robust cybersecurity measures, and innovative materials.
Despite these threats, continued advancements in nanotechnology, artificial intelligence, and flexible electronics may eventually lead to widespread adoption of electronic skin, revolutionizing healthcare, robotics, and wearable technology.