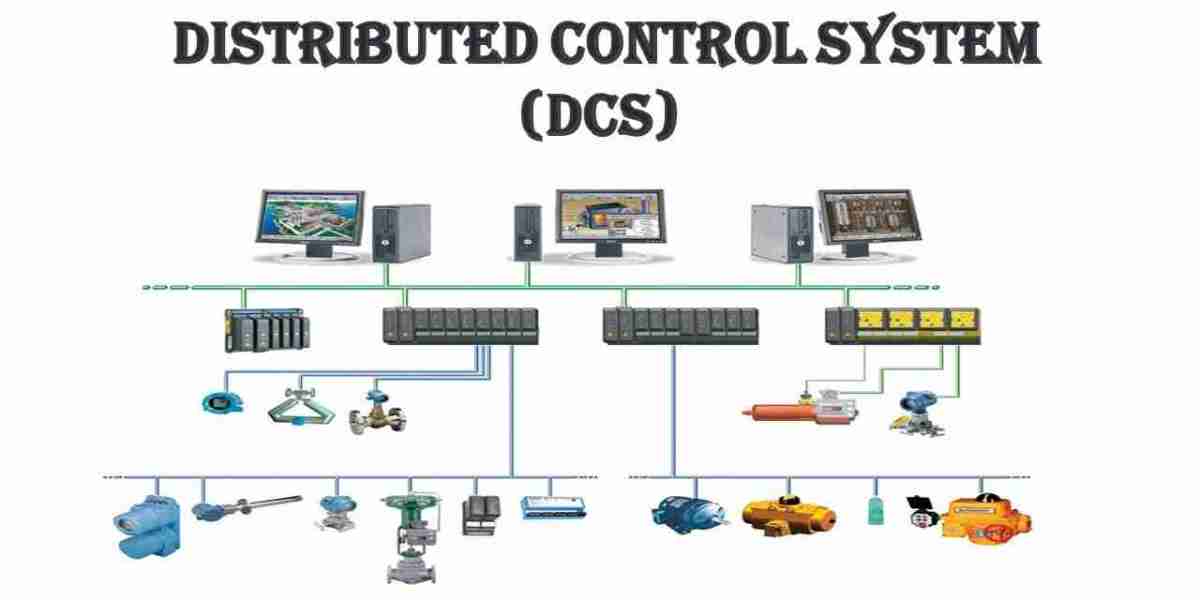
Introduction
The Distributed Control Systems market is playing a pivotal role in the transformation of traditional industries into smart factories. As digitalization accelerates, DCS is evolving to integrate AI, IoT, cloud computing, and real-time data analytics, driving efficiency, automation, and intelligent decision-making. This article explores how DCS contributes to the evolution of smart factories and industrial digitalization, highlighting key trends, challenges, and future opportunities.
Role of DCS in Smart Factories
1. Seamless Automation and Process Control
DCS enables centralized and decentralized control of manufacturing processes, ensuring real-time data exchange between different production units. This enhances automation, consistency, and operational efficiency in smart factories.
2. Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Modern DCS systems leverage AI and machine learning algorithms to optimize production workflows, predict equipment failures, and enable self-learning process adjustments for maximum efficiency.
3. IoT-Driven Connectivity and Smart Sensors
The integration of Industrial IoT (IIoT) sensors with DCS allows for real-time monitoring of machinery, environmental conditions, and product quality. This connectivity reduces downtime, improves predictive maintenance, and enhances productivity.
4. Cybersecurity and Data Protection
As smart factories become more connected, cybersecurity becomes a critical challenge. DCS solutions are incorporating advanced encryption, firewalls, and AI-driven threat detection to safeguard industrial networks and sensitive data.
5. Cloud Computing and Edge Processing
Cloud-based DCS solutions enable remote monitoring, real-time analytics, and collaboration across multiple facilities. Additionally, edge computing allows for faster data processing at the factory level, reducing latency and improving decision-making.
Challenges in DCS Adoption for Smart Factories
1. High Implementation Costs
Deploying AI-powered and IoT-enabled DCS requires significant investment in infrastructure, training, and integration with existing systems. Many small and mid-sized enterprises (SMEs) find the costs prohibitive.
2. Interoperability with Legacy Systems
Many manufacturers still operate traditional PLC-based systems that may not be fully compatible with modern cloud-connected DCS solutions. Achieving seamless integration remains a challenge.
3. Data Overload and Management Complexity
Smart factories generate massive volumes of data, requiring efficient data storage, processing, and analytics capabilities. Managing and making sense of this data poses a challenge for organizations.
4. Skilled Workforce Shortage
The demand for professionals skilled in AI-driven automation, cybersecurity, and data analytics is rising. Many industries face a shortage of qualified personnel to operate and maintain advanced DCS solutions.
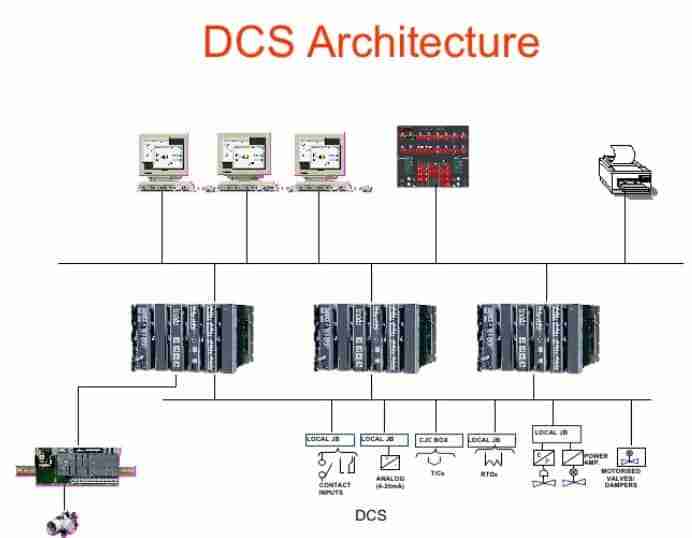
Future Trends and Opportunities
1. AI-Powered Decision Making
The next generation of DCS solutions will incorporate AI-driven decision-making, enabling factories to self-optimize processes, reduce waste, and enhance quality control.
2. Digital Twins for Smart Manufacturing
DCS is increasingly being used to develop digital twin models, allowing manufacturers to simulate, analyze, and optimize operations in a virtual environment before implementation.
3. 5G Connectivity for Industrial Automation
The deployment of 5G networks will enhance the speed and reliability of real-time data transmission, further improving DCS capabilities in smart factories.
4. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
With growing emphasis on sustainability, DCS solutions are integrating energy-efficient technologies, carbon footprint monitoring, and renewable energy optimization in manufacturing processes.
Conclusion
The Distributed Control Systems market is at the forefront of industrial digitalization and smart factory evolution. By integrating AI, IoT, cloud computing, and cybersecurity, DCS is enabling greater automation, efficiency, and data-driven decision-making. While challenges such as high costs, integration issues, and workforce shortages persist, continued innovation in AI-powered automation, digital twins, and 5G connectivity will shape the future of smart manufacturing. Organizations that invest in DCS-driven digital transformation will gain a competitive edge in the Industry 4.0 era.