Introduction
The rugged thermal camera market has witnessed significant growth due to increasing demand across industries such as defense, security, industrial inspection, and environmental monitoring. As thermal imaging technology advances, the supply chain and manufacturing processes play a crucial role in ensuring the availability of high-quality, durable cameras capable of performing in extreme conditions. This article explores the supply chain dynamics, manufacturing challenges, and key factors shaping the production of rugged thermal cameras.
Supply Chain Overview
The supply chain of rugged thermal cameras involves multiple stages, from raw material sourcing to final product distribution. Each stage plays a critical role in ensuring product quality, cost efficiency, and timely delivery. The major components of the supply chain include:
1. Raw Material Sourcing
Optical Components: High-quality infrared lenses, germanium optics, and other specialized materials are essential for accurate thermal imaging.
Semiconductors and Sensors: Microbolometer sensors, which detect infrared radiation, are key components sourced from specialized manufacturers.
Durable Housing Materials: Rugged thermal cameras require robust casings made from high-grade aluminum, stainless steel, or composite materials to withstand harsh environments.
2. Component Manufacturing and Assembly
Sensor Fabrication: Leading manufacturers invest in semiconductor fabrication facilities to produce high-performance thermal sensors.
Optics and Electronics Assembly: Infrared optics are combined with electronic circuitry to enhance signal processing and image clarity.
Durability Enhancements: Cameras undergo rigorous testing to ensure resistance to extreme temperatures, vibrations, and water exposure.
3. Quality Control and Testing
Environmental Testing: Cameras are tested under varying temperatures, humidity, and pressure conditions to ensure reliability.
Calibration and Accuracy Checks: Thermal imaging accuracy is verified through precision calibration techniques.
Regulatory Compliance: Manufacturers adhere to industry standards and certifications, such as ISO, MIL-STD, and CE, to meet global market requirements.
4. Distribution and Logistics
Global Supply Chains: Manufacturers coordinate with global distributors to ensure the availability of rugged thermal cameras in multiple regions.
Customization and Integration: Some industries require custom-built solutions, leading manufacturers to offer specialized camera configurations.
After-Sales Support: Companies provide maintenance, calibration services, and software updates to enhance the longevity of thermal cameras.
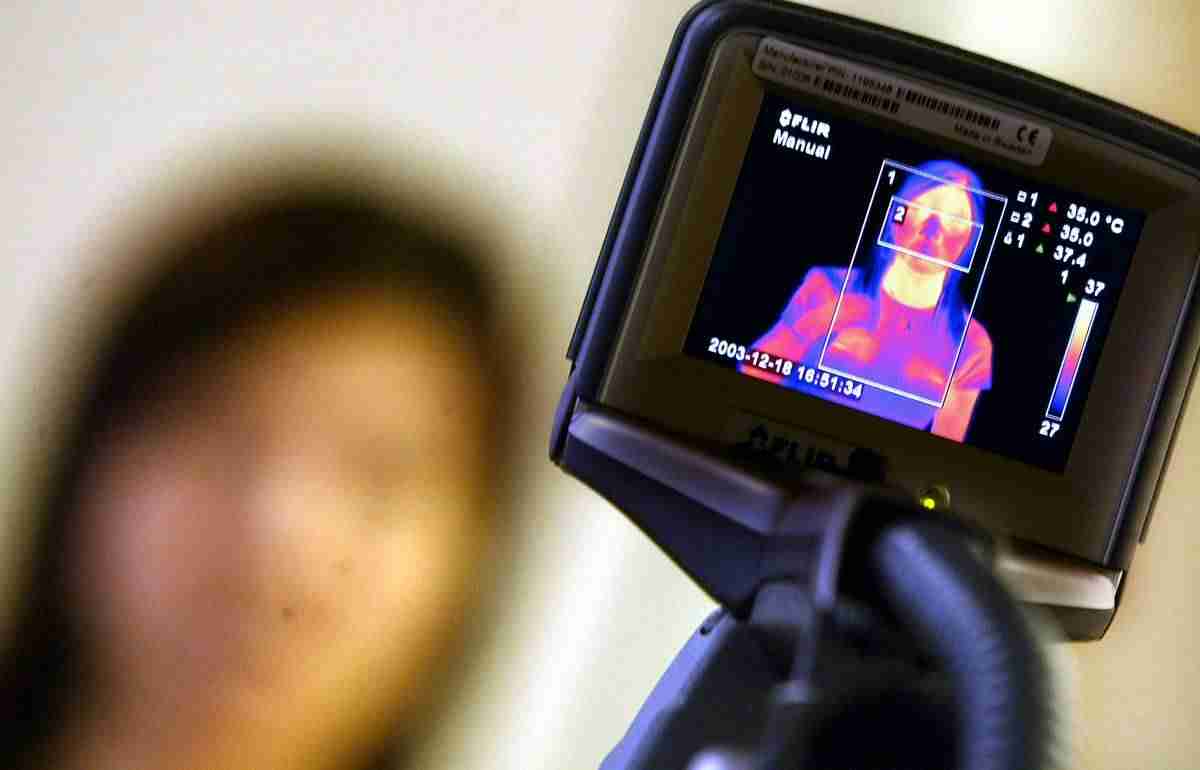

Manufacturing Challenges and Solutions
Despite the growing demand for rugged thermal cameras, manufacturers face several challenges in production. Key challenges include:
1. High Production Costs
Solution: Automation in manufacturing, improved sensor fabrication techniques, and economies of scale help reduce production costs.
2. Component Shortages
Solution: Diversifying the supplier base and investing in localized production facilities can mitigate supply chain disruptions.
3. Technological Advancements and R&D Costs
Solution: Continuous investment in research and development (R&D) ensures innovative designs and improved camera performance, keeping manufacturers competitive in the market.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Solution: Strict adherence to international safety and security standards ensures market approval and enhances consumer trust.
Future Trends in Rugged Thermal Camera Manufacturing
The rugged thermal camera market is evolving with advancements in manufacturing techniques and supply chain optimizations. Key future trends include:
Integration of AI and Machine Learning: AI-powered thermal cameras improve object detection, anomaly identification, and automation in industrial applications.
3D Printing in Camera Prototyping: Additive manufacturing techniques accelerate design innovation and production efficiency.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices: Companies are investing in eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient production techniques.
Enhanced Miniaturization: The development of compact, lightweight thermal cameras with improved performance is expected to drive demand in various industries.
Conclusion
The supply chain and manufacturing processes of rugged thermal cameras are critical to ensuring product reliability and efficiency in extreme environments. From raw material procurement to quality testing and global distribution, each stage of the supply chain plays a crucial role in shaping the market. With ongoing technological advancements, manufacturers are focused on reducing production costs, improving camera performance, and addressing supply chain challenges. As demand continues to grow across industries, the rugged thermal camera market is expected to witness further innovation and expansion.