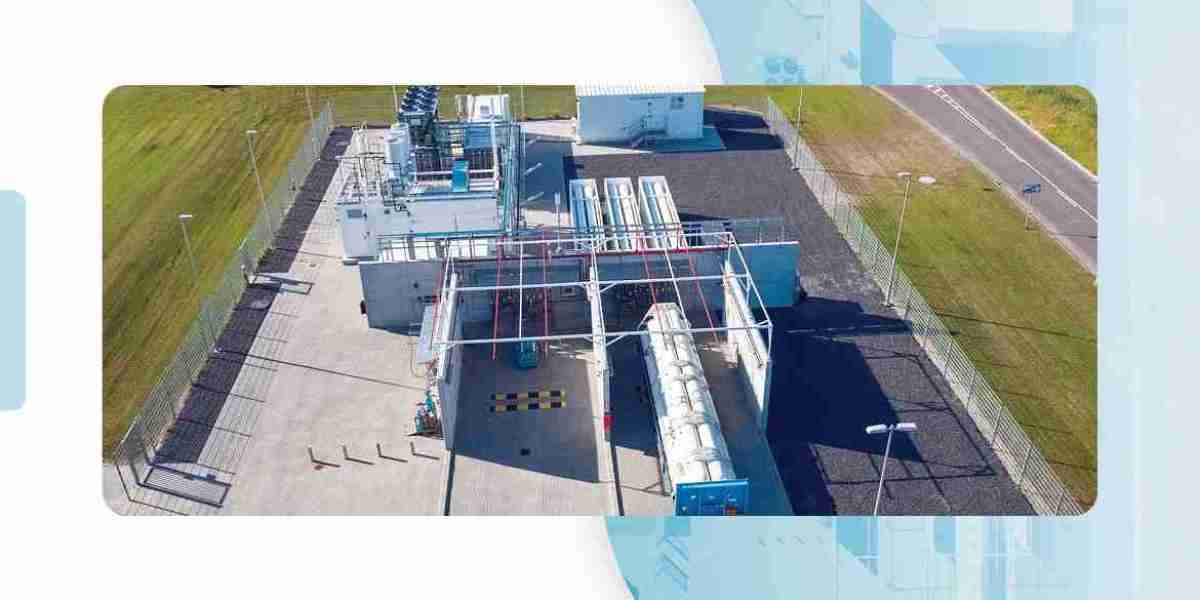
Hydrogen electrolyzers are gaining momentum as a key technology for clean energy transition. They play a crucial role in producing green hydrogen, which is essential for reducing carbon emissions across industries. However, despite the promising potential, the hydrogen electrolyzer market faces several significant threats that hinder its widespread adoption and long-term sustainability. These threats include economic challenges, supply chain disruptions, technological limitations, policy uncertainties, and competitive risks.
1. Rising Costs and Economic ChallengesThe production and deployment of hydrogen electrolyzers require substantial investment. High capital expenditure (CAPEX) and operational costs remain a major barrier to market expansion. The cost of materials such as iridium, platinum, and other rare metals essential for electrolyzer construction continues to fluctuate, leading to pricing instability. Additionally, the energy-intensive nature of electrolyzers results in significant electricity costs, which can vary based on location and energy source availability. Without consistent cost reductions and improved efficiency, the market may struggle to achieve widespread commercial viability.
2. Supply Chain Disruptions and Material ShortagesThe global supply chain for electrolyzer components faces several challenges, including raw material shortages and logistical disruptions. The dependency on scarce minerals and geopolitical risks in key supplier regions add to market volatility. Furthermore, transportation bottlenecks and trade restrictions contribute to delays in electrolyzer production and deployment. These issues not only increase costs but also create uncertainties in scaling up manufacturing capacity to meet rising demand.
3. Technological Limitations and Infrastructure GapsAlthough hydrogen electrolyzer technology has advanced significantly, certain technical limitations remain. Current electrolyzer efficiency levels, durability concerns, and maintenance costs pose challenges for large-scale deployment. The integration of electrolyzers into existing energy infrastructure also requires extensive modifications and new investments, particularly in regions lacking hydrogen storage and distribution networks. Without significant technological breakthroughs, the adoption of electrolyzers at a global scale may remain constrained.
4. Policy Uncertainties and Regulatory HurdlesGovernment policies play a crucial role in shaping the hydrogen electrolyzer market. However, inconsistencies in regulatory frameworks, shifting incentives, and changing political priorities pose a significant threat. Many countries are still formulating hydrogen strategies, leading to delays in policy implementation. Furthermore, varying carbon pricing mechanisms, subsidy structures, and renewable energy mandates create an uneven playing field for industry players. A lack of clear, long-term regulatory commitments could slow down investment and innovation in the sector.
5. Competition from Alternative Energy SourcesWhile green hydrogen is touted as a clean energy solution, it faces stiff competition from other renewable energy technologies. Battery storage, direct electrification, and biofuels present alternative pathways for decarbonization. Many industries may opt for cheaper or more established options instead of investing in hydrogen electrolyzers. Additionally, fossil-fuel-based hydrogen (blue and grey hydrogen) continues to dominate the market due to its lower production costs, further slowing the transition to electrolyzer-based hydrogen production.
6. Environmental and Public Perception Issues Despite being a clean energy solution, hydrogen electrolyzer technology is not without environmental concerns. The water-intensive nature of electrolyzers raises sustainability issues in water-scarce regions. Moreover, the electricity source for electrolyzers significantly impacts their carbon footprint—if sourced from fossil-fuel-based grids, the overall emissions reduction benefits may be limited.
Conclusion The hydrogen electrolyzer market holds immense promise for the global energy transition, but several threats must be addressed to ensure its long-term success. Economic challenges, supply chain vulnerabilities, technological limitations, policy uncertainties, competitive pressures, and environmental concerns all pose significant hurdles to the industry’s growth. Overcoming these threats requires coordinated efforts from governments, businesses, and researchers to drive innovation, establish stable policies, and improve infrastructure. By tackling these challenges head-on, the hydrogen electrolyzer market can play a vital role in achieving a sustainable, low-carbon future.
rohinishinde
234 وبلاگ نوشته ها