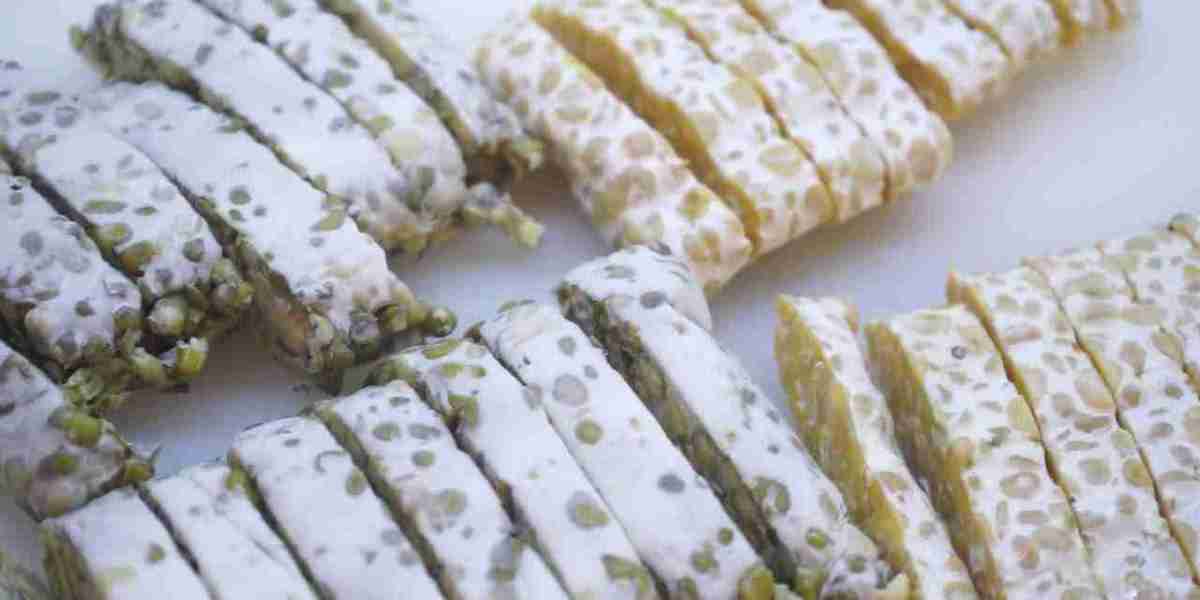
Tempeh, a popular plant-based protein made from fermented soybeans, has gained global traction as more people turn to vegetarian, vegan, and flexitarian diets. However, despite its rising popularity, the tempeh market faces several restraints that may hinder its growth in the coming years. This article explores the key barriers impacting the tempeh market, from production challenges to consumer awareness.
Tempeh Market Restraints: Limited Consumer Awareness
One of the biggest restraints in the tempeh market is the lack of consumer awareness in many regions. While tempeh is well known in Southeast Asia and parts of the United States, many consumers in other regions may not be familiar with it. Educating consumers about tempeh’s nutritional benefits, versatility, and cultural significance is crucial to expanding its market presence. Without adequate awareness campaigns and marketing strategies, the market may struggle to reach its full potential, limiting consumer adoption.
Tempeh Market Restraints: Limited Availability in Mainstream Retailers
Tempeh's availability is still somewhat limited in many mainstream grocery stores and supermarkets outside of specialized health food retailers. While the market for plant-based products is expanding, tempeh may not be as accessible to all consumers due to limited distribution. Many regions still lack sufficient retail presence for tempeh products, making it difficult for consumers to access it easily. Expanding the availability of tempeh in mainstream outlets will be crucial for growth, but distribution challenges present a significant barrier.
Tempeh Market Restraints: Production Complexity and Cost
The production of tempeh involves a fermentation process, which requires specialized equipment and technical knowledge. This can make scaling up production difficult for smaller manufacturers, especially in regions where fermentation processes are not widely understood. The need for fermentation also adds to production costs, potentially limiting price competitiveness with other plant-based protein sources like tofu or seitan. High production costs, especially in emerging markets, may hinder market expansion, as consumers may opt for cheaper alternatives.
Tempeh Market Restraints: Taste and Texture Preferences
Despite its health benefits, tempeh’s taste and texture are not universally liked by all consumers. Some people find its nutty flavor and firm texture to be off-putting, especially those who are used to more familiar meat substitutes like tofu or plant-based meat products. Overcoming this sensory barrier is essential for encouraging wider adoption. Manufacturers will need to invest in product innovation, offering flavored or pre-marinated tempeh options that cater to a broader range of taste preferences.
Tempeh Market Restraints: Competition from Other Plant-Based Proteins
The tempeh market faces intense competition from other plant-based protein sources like tofu, seitan, and legumes. These alternatives are often more familiar to consumers and can be easier to prepare and incorporate into meals. While tempeh is highly nutritious, the market must compete against established plant-based products that have already achieved significant consumer loyalty. The rise of plant-based meat products, which closely mimic the taste and texture of animal meat, also presents competition for tempeh as a meat substitute.
Tempeh Market Restraints: Cultural and Regional Differences
Tempeh, while rooted in Southeast Asian cuisine, is not traditionally a part of many other cultures. As a result, its acceptance may be limited in regions where plant-based protein sources are less common. In some countries, consumers may be more inclined to choose familiar alternatives, making it harder for tempeh to gain traction. Understanding regional food preferences and cultural attitudes toward plant-based diets will be crucial for overcoming this barrier. Introducing tempeh as part of fusion cuisine or as a global food trend may help to introduce it to new markets.
Tempeh Market Restraints: Regulatory and Labeling Challenges
In some countries, the regulatory environment and labeling requirements for plant-based foods may be restrictive or unclear. Tempeh is often marketed as a vegan or vegetarian protein, but regulations around the labeling of plant-based foods are not always consistent. Misleading labeling or the inability to market tempeh as a "health food" or "sustainable option" in certain regions could hurt its market penetration. Manufacturers and regulators must collaborate to ensure clear, standardized labeling that helps educate consumers and builds trust in tempeh as a nutritious food choice.
Tempeh Market Restraints: Price Sensitivity in Emerging Markets
Price sensitivity remains a significant restraint for tempeh in emerging markets. While tempeh is a cost-effective protein source compared to animal-based meat, its price can still be a barrier for lower-income consumers, especially when compared to other local plant-based options. As the market for tempeh grows, there will be pressure to keep prices competitive to attract consumers in emerging economies, where plant-based protein is often considered a premium product. Developing cost-effective production and distribution strategies will be key to overcoming this restraint.
Tempeh Market Restraints: Supply Chain and Ingredient Sourcing Challenges
The global supply chain for ingredients used in tempeh production, particularly soybeans, is vulnerable to disruption due to factors such as climate change, trade policies, and geopolitical tensions. Any supply chain disruptions can result in price volatility and shortages of raw materials, affecting the cost and availability of tempeh. Companies must establish resilient supply chains and explore alternative ingredient sources to ensure consistent production of tempeh products.
Tempeh Market Restraints: Consumer Education and Recipe Accessibility
In many regions, tempeh is still viewed as an unfamiliar ingredient that requires specific cooking knowledge. Unlike more common plant-based proteins, tempeh is often seen as difficult to cook or incorporate into everyday meals. Without a clear understanding of how to prepare tempeh and integrate it into various recipes, potential consumers may be reluctant to try it. Providing easy-to-follow recipes and cooking demonstrations will be critical in reducing the barrier of entry for new customers.
Conclusion
The tempeh market faces numerous restraints, including limited consumer awareness, competition from other plant-based proteins, and challenges in production and distribution. However, by addressing these obstacles through innovative marketing, product diversification, and educational initiatives, the tempeh market has the potential to overcome these barriers and expand its reach. The key to success lies in making tempeh more accessible, affordable, and appealing to a broader audience. As consumer interest in plant-based foods continues to grow, tempeh could play an important role in the global shift toward sustainable, plant-based diets.