Strains, sprains, and soft tissue injuries are common types of musculoskeletal injuries that affect people of all ages and activity levels. Whether you are an athlete, a busy professional, or someone who enjoys physical activity, understanding these injuries and how to treat them can help you recover more efficiently. In this complete guide, we will delve into the nature of these injuries, how they occur, the symptoms, and the most effective treatment options, including the use of medications such as Carisoprodol (found in products like Prosoma and Pain O Soma).
What Are Strains and Sprains?
Strains and sprains are often confused, but they refer to different types of injuries involving the musculoskeletal system.
Strain: A strain occurs when a muscle or tendon (the tissue that connects muscles to bones) is stretched or torn. This can happen when a muscle is overstretched or overused. Strains commonly affect the lower back, hamstrings, and shoulders.
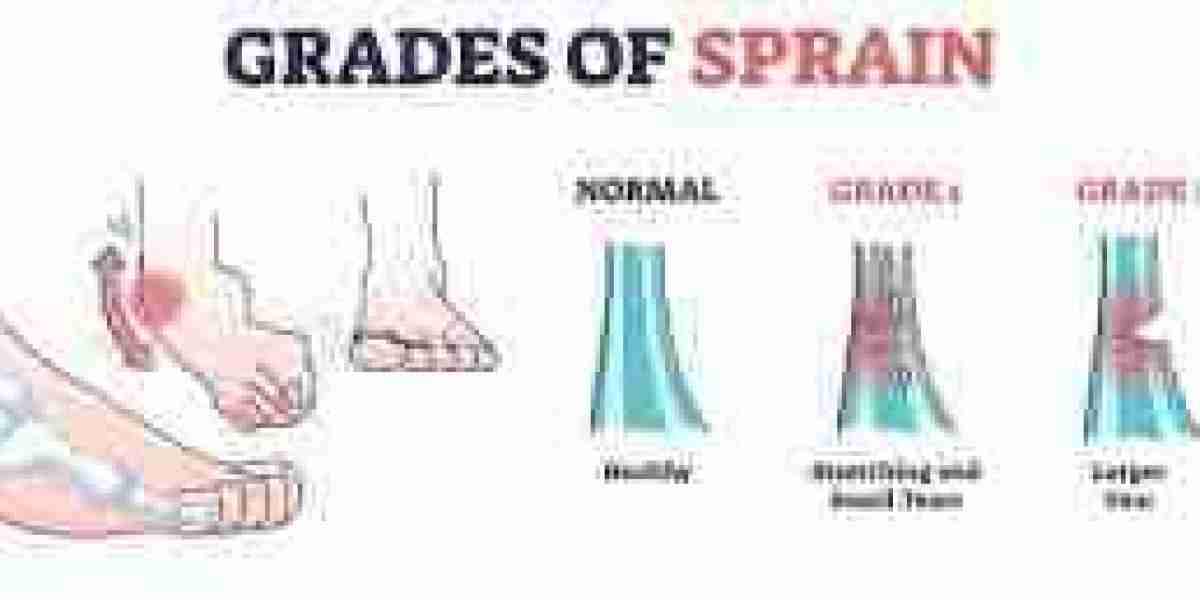
Sprain: A sprain is an injury to a ligament (the tissue connecting bones to other bones), often caused by overstretching or tearing due to sudden movements or trauma. Sprains commonly occur in joints like the ankles, knees, and wrists.
Both strains and sprains can vary in severity from mild to severe, with different levels of pain, swelling, and restricted movement.
Soft Tissue Injuries
Soft tissue injuries include damage to muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Unlike bone fractures, soft tissue injuries typically involve stretching or tearing of these connective tissues. These injuries can range from minor overstretching to more severe tears that require medical attention. Soft tissue injuries may occur due to:
- Overuse: Repeating the same movement over time can cause stress on the muscles and tendons, leading to wear and tear.
- Trauma: A sudden blow, twist, or fall can damage soft tissues.
- Improper technique: Incorrect posture or movement during physical activities can strain muscles or ligaments.
Some common soft tissue injuries include:
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of a tendon caused by repetitive use or strain.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs (bursae) that cushion joints.
- Muscle tears: Partial or complete ruptures of muscle fibers.
Symptoms of Strains, Sprains, and Soft Tissue Injuries
The symptoms of strains, sprains, and soft tissue injuries can vary depending on the severity and location of the injury. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: Ranging from mild to severe, pain is usually localized to the affected area.
- Swelling: Inflammation may occur, particularly in the case of sprains.
- Bruising: A sign of blood vessels being damaged in the affected area.
- Restricted movement: The injured area may become stiff, and movement may be difficult or painful.
- Muscle weakness: Injuries to muscles or tendons may cause weakness in the affected limb.
If you experience severe pain, inability to move the affected area, or signs of a serious injury (e.g., broken bones), it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Treatment of Strains, Sprains, and Soft Tissue Injuries
The treatment for strains, sprains, and soft tissue injuries typically follows a protocol known as R.I.C.E., which stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. However, depending on the severity of the injury, additional treatments may be necessary.
1. Rest:
Allow the injured area to rest for 24-48 hours. Avoid putting weight on it or engaging in activities that could aggravate the injury.
2. Ice:
Applying ice to the injured area helps reduce inflammation and numbs the pain. Apply ice for 20-30 minutes every 2-3 hours during the first 48 hours after the injury.
3. Compression:
Using an elastic bandage or compression wrap can help reduce swelling and support the injured area.
4. Elevation:
Elevating the injured limb above the level of the heart helps reduce swelling by promoting better circulation.
Medications for Managing Pain and Inflammation
Pain management is crucial when recovering from strains, sprains, or other soft tissue injuries. Anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or aspirin, are often used to reduce pain and swelling. In more severe cases, muscle relaxants and prescription pain relievers may be required.
One such muscle relaxant is Carisoprodol, which is commonly found in medications like Prosoma and Pain O Soma. Carisoprodol works by affecting the central nervous system to relieve muscle spasms and reduce pain.
Carisoprodol: How It Works
Carisoprodol is a muscle relaxant that helps reduce muscle spasms and tension, which can occur with strains, sprains, and other soft tissue injuries. It acts on the central nervous system, blocking pain signals and inducing a calming effect on the muscles. Carisoprodol is generally prescribed for short-term use, typically in conjunction with physical therapy and rest.
Prosoma and Pain O Soma are two popular brand names of Carisoprodol. These medications are typically prescribed for muscle pain, spasms, and tension caused by soft tissue injuries. By alleviating muscle spasms, Carisoprodol helps restore movement and flexibility, facilitating quicker recovery.
Dosage of Carisoprodol
The typical dosage for Carisoprodol varies depending on the severity of the injury and the patient's medical history. For most individuals, the recommended dose is 250 mg to 350 mg, taken 3 times a day and at bedtime.
It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions when using Carisoprodol. While this medication is effective in relieving pain and muscle spasms, it should not be used for prolonged periods due to potential dependency and side effects.
Prosoma and Pain O Soma: Effective Solutions for Soft Tissue Injury Pain
Prosoma and Pain O Soma are both effective medications used to treat muscle pain and spasms caused by soft tissue injuries. The key ingredient in both medications is Carisoprodol, which provides relief from pain and discomfort associated with strains, sprains, and other muscle injuries.
Prosoma: Prosoma is a widely prescribed medication for acute musculoskeletal pain. The active ingredient, Carisoprodol, works by relaxing the muscles and reducing pain and discomfort. This medication is commonly used for short-term treatment in combination with other therapies such as physical therapy or rest.
Pain O Soma: Similar to Prosoma, Pain O Soma also contains Carisoprodol. It is often used to treat acute muscle pain or spasms resulting from soft tissue injuries like strains and sprains. This medication helps reduce muscle stiffness and restore mobility, making it easier for patients to engage in rehabilitation exercises.
Both medications are typically used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes rest, physical therapy, and other interventions to support healing. Additionally, HealthCurePills offers an exciting promotion where you can get 20 pills free when purchasing Pain O Soma or Prosoma, helping to reduce the overall cost of treatment.
Prevention of Strains, Sprains, and Soft Tissue Injuries
While it may not always be possible to avoid soft tissue injuries, there are several strategies you can adopt to reduce your risk:
- Warm-up and cool down: Before and after exercise, take time to warm up and cool down your muscles to prevent strain.
- Proper technique: Use proper posture and technique during physical activities to minimize the risk of injury.
- Strengthening exercises: Regularly perform exercises to build strength and flexibility, particularly in areas that are prone to injury.
- Wear proper footwear: Shoes that provide good support can reduce the risk of sprains, especially in activities that involve running or jumping.
- Avoid overtraining: Rest and recover adequately between intense physical activities to prevent overuse injuries.
Conclusion
Strains, sprains, and soft tissue injuries are common, but with prompt treatment and care, most individuals can recover fully and return to their normal activities. The R.I.C.E. method, along with pain management options like Carisoprodol (found in Prosoma and Pain O Soma), can provide significant relief. Additionally, preventive measures can help minimize the risk of injury in the future. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of treatment for your injury and ensure a full recovery.