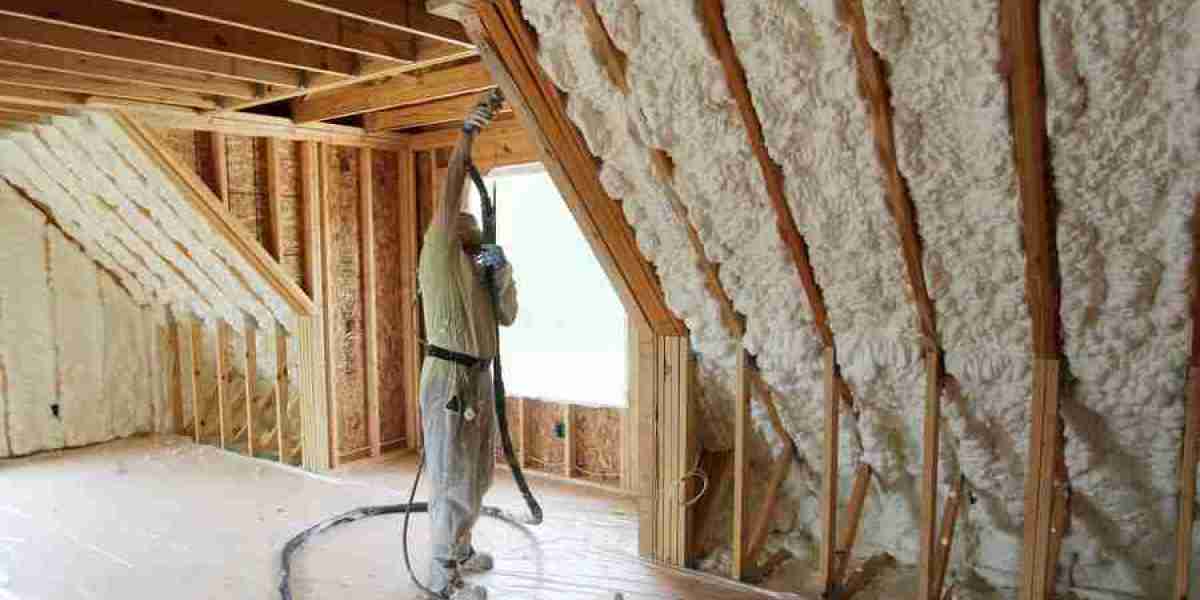
The global foam insulation market has grown in size and relevance, primarily due to the increasing demand for energy-efficient building materials and sustainable construction practices. As a vital component in reducing heat loss and enhancing energy efficiency, foam insulation plays a significant role in various sectors, including construction, manufacturing, and automotive. Despite the attractive growth prospects, new entrants face several entry barriers that may limit their ability to successfully enter the market.
Understanding these barriers is key for businesses looking to make their mark in the foam insulation industry. In this article, we will explore the key market entry barriers and how businesses can overcome them.
1. Capital Investment Requirements
One of the primary barriers to entry in the foam insulation market is the high initial capital required to set up manufacturing plants and acquire advanced machinery. Companies seeking to enter the market need significant upfront investments in order to ensure that production processes comply with industry standards and to access raw materials. These investments are often too costly for smaller companies or startups, posing a considerable barrier. Additionally, manufacturing equipment, such as extruders and foaming machines, can be expensive to purchase and maintain.
2. Stringent Regulations and Standards
Another major challenge for new entrants is the strict regulatory framework governing the production and distribution of foam insulation materials. Governments in different regions enforce regulations concerning the environmental impact of insulation materials, such as the use of non-toxic materials, fire safety standards, and health concerns related to certain chemicals. Navigating these standards requires companies to invest in research and development to ensure their products comply with local and international regulations. Failing to meet these standards could result in product recalls, legal consequences, or damage to a company’s reputation.
3. Established Competition
The foam insulation market is highly competitive, with several large players controlling a significant portion of the market share. These established companies have strong brand recognition, loyal customer bases, and well-established distribution networks that can be challenging to compete against. New companies may find it difficult to break into the market due to this overwhelming competition, especially if they lack the resources to engage in large-scale marketing campaigns or offer highly differentiated products.
4. Supply Chain Challenges
Another entry barrier that new entrants face is navigating the complexities of the supply chain. Foam insulation manufacturing relies on a range of raw materials, including petroleum-based products such as polyurethane and polystyrene. Supply chain disruptions, fluctuations in raw material prices, and logistical challenges can hinder the production process and cause delays. New market entrants may struggle to secure reliable and cost-effective raw materials, which can affect their ability to produce high-quality products and compete with established players.
5. Technological Expertise and Innovation
Foam insulation is a technically complex product that requires a high level of expertise in chemistry, manufacturing processes, and sustainability practices. Companies looking to enter the market must invest in research and development to stay competitive and meet the ever-evolving demands for energy-efficient products. New entrants with limited technological expertise or insufficient R&D resources may struggle to keep up with innovations in foam production methods, such as the development of environmentally friendly alternatives or improved insulation properties.
6. Brand Trust and Reputation
Brand trust and reputation are important assets for companies entering the foam insulation market. Established companies have spent years building customer loyalty based on the reliability and performance of their products. New entrants may struggle to gain trust among customers, as foam insulation is a product typically relied upon for long-term performance in energy conservation. Establishing a reputation for product quality, customer service, and sustainability can take time, making it challenging for newcomers to build a loyal customer base.
7. High Distribution and Logistics Costs
Given that foam insulation products are typically bulky and require careful handling, new market players often face high distribution and logistics costs. They must establish efficient distribution channels to compete with established players who have more robust networks in place. These costs can make it more difficult for smaller companies to offer competitive pricing or achieve desirable profit margins.
Conclusion
While the foam insulation market offers significant opportunities for growth, the barriers to entry can be formidable for new entrants. To successfully enter and compete in this space, businesses must carefully navigate capital investment requirements, regulatory standards, and intense competition. Additionally, overcoming challenges such as supply chain complexity, technological expertise, and high distribution costs will require businesses to leverage innovation, strong partnerships, and sound financial strategies. Companies that are able to differentiate themselves through product quality, environmental sustainability, and customer trust will be well-positioned for success in the foam insulation market.