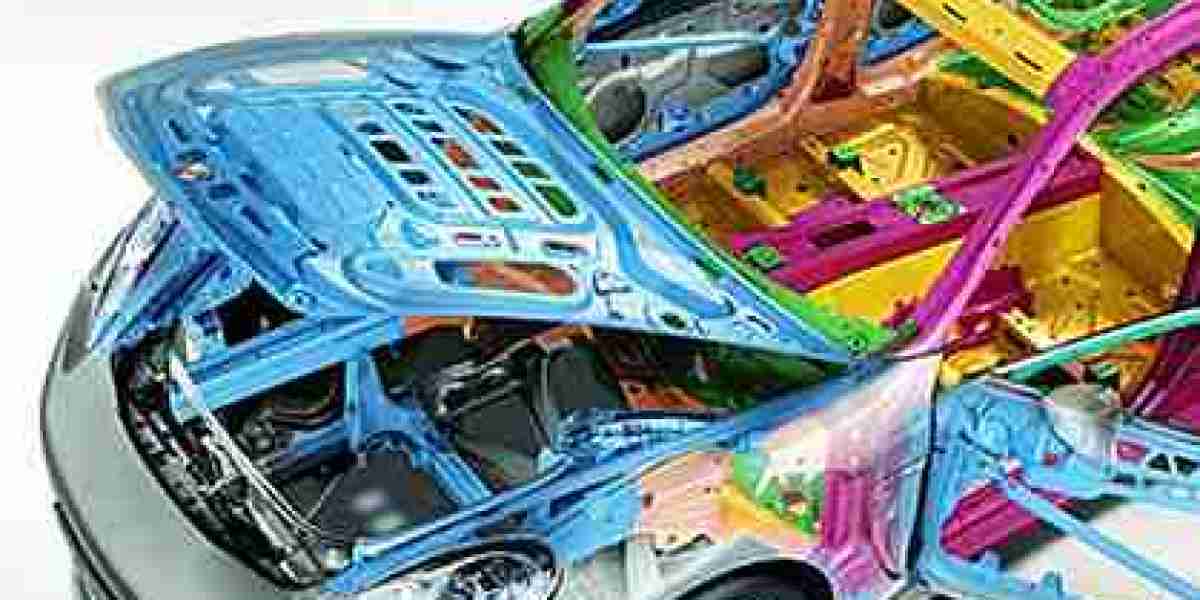
The automotive industry is witnessing significant advancements as the demand for fuel-efficient and eco-friendly vehicles continues to rise. A major contributor to achieving these goals is the use of automotive lightweight materials, which are revolutionizing vehicle manufacturing. Lightweight materials not only improve fuel efficiency but also contribute to the reduction of carbon emissions, enhance vehicle performance, and ensure compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
Key Developments in Automotive Lightweight Materials
The automotive lightweight materials market has been evolving rapidly, with several materials making their way into mainstream production. Traditional materials like steel and aluminum are being replaced or combined with advanced composites, polymers, and innovative metals, opening up new possibilities for manufacturers. Here are some of the key developments in the automotive lightweight materials market:
Adoption of High-Strength Steel (HSS): One of the most significant developments in recent years has been the widespread use of high-strength steel (HSS) in the automotive sector. HSS allows manufacturers to reduce the weight of vehicles while maintaining strength and safety standards. It is especially beneficial for structural components like chassis and body frames. The material’s ability to withstand extreme stress makes it a favorite for manufacturers seeking durability without adding weight.
Growth of Aluminum Usage: Aluminum is another lightweight material gaining traction in automotive manufacturing. Aluminum offers a balance between weight reduction and strength. It is particularly effective in body panels, engine blocks, and wheels. Its lightweight properties help to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and offer better vehicle handling. As more automakers shift toward electric and hybrid vehicles, aluminum plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and range of these vehicles.
Composite Materials: Carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) and glass fiber-reinforced polymer (GFRP) are becoming more common in the automotive sector due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratios. CFRP, although expensive, is utilized in high-performance vehicles, especially in sports cars. GFRP is more cost-effective and is used in mass-market applications, particularly in electric vehicles (EVs), where weight reduction is critical for battery performance. These materials offer high stiffness and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for automotive applications.
Magnesium Alloys: Magnesium is the lightest structural metal, making it an attractive option for the automotive industry. Although it has not yet been adopted widely, the use of magnesium alloys is expected to increase in the coming years. Magnesium alloys can be used in a variety of automotive components, such as wheels, engine blocks, and body panels. However, issues related to material cost and processing technologies have slowed the widespread adoption of magnesium alloys. Advancements in manufacturing processes and reductions in material costs could drive future growth.
Development of Biocomposites: As the automotive industry embraces sustainability, biocomposites made from renewable resources like plant fibers are gaining attention. These biocomposites not only reduce weight but also offer an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional materials. Manufacturers are exploring the use of biocomposites in non-structural components like interior panels, dashboards, and upholstery. The growing focus on sustainability, along with improvements in biocomposite material properties, is expected to fuel the expansion of this segment in the coming years.
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing has been a game-changer in various industries, and automotive manufacturing is no exception. The ability to print complex parts with lightweight materials like plastic and metals is revolutionizing the way vehicles are produced. Additive manufacturing allows for greater customization, faster prototyping, and lighter parts with minimal waste. This technology is particularly beneficial for the production of components with intricate geometries that would be difficult to achieve using traditional manufacturing methods.
Improved Recycling Technologies: One of the challenges with lightweight materials, particularly composite materials, is their recyclability. However, advancements in recycling technologies are helping to address this issue. Manufacturers are investing in technologies that allow for the recycling of materials like carbon fiber and aluminum, thus contributing to a circular economy. This not only helps in reducing production costs but also aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability in the automotive industry.
Conclusion
The automotive lightweight materials market is on the brink of significant growth as the industry adapts to evolving consumer preferences, environmental concerns, and regulatory pressures. The increasing use of materials like high-strength steel, aluminum, composites, and magnesium alloys is not only reducing vehicle weight but also enhancing performance and safety. Additionally, sustainable materials like biocomposites and the implementation of advanced manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing are expected to further transform the market. As these technologies and materials continue to develop, the future of the automotive lightweight materials market looks promising.