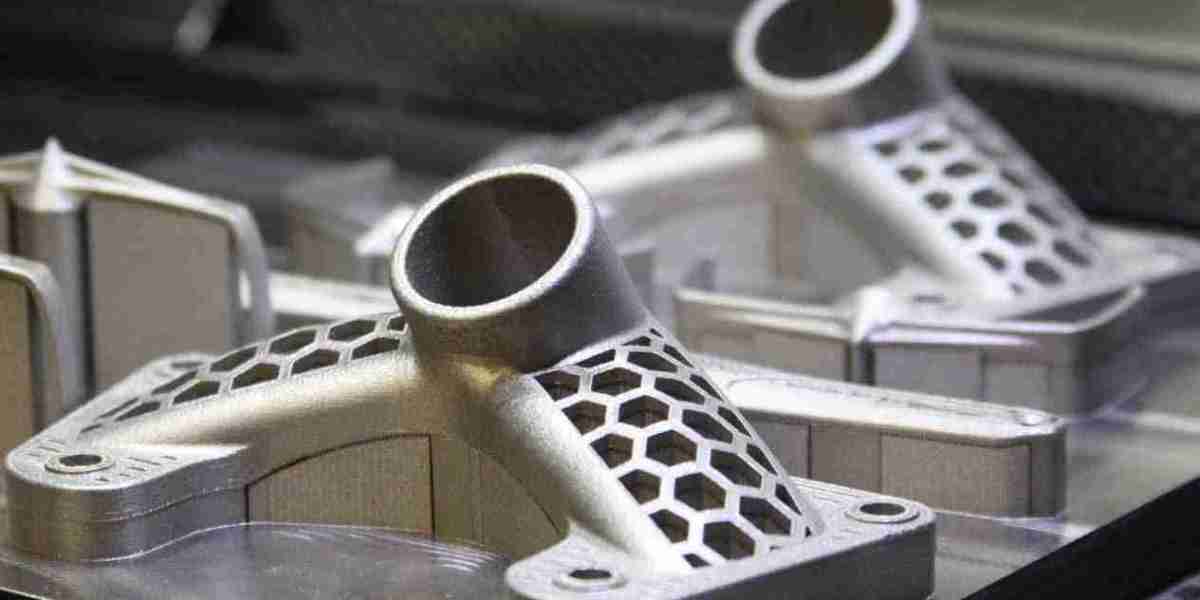
The 3D printing stainless steel market is evolving rapidly, driven by technological innovations, shifting industry demands, and market disruptions. Stainless steel, known for its durability, corrosion resistance, and strength, is a preferred material for a wide range of applications, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and industrial manufacturing. This insight explores the key innovations fueling growth in the market, the restraints hindering its progress, and the potential disruptions that could shape its future.
Innovations Driving Market Growth
Improved Printing Technology
One of the key innovations shaping the 3D printing stainless steel market is the advancement of printing technologies. Traditional additive manufacturing processes, such as fused deposition modeling (FDM), have evolved significantly, with more sophisticated techniques like selective laser melting (SLM) and direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) becoming the preferred methods for producing stainless steel parts. These processes enable the creation of highly detailed and complex geometries that traditional manufacturing methods cannot achieve. Innovations in laser-based technology have improved the precision and surface quality of 3D printed stainless steel, making it suitable for high-performance applications in industries like aerospace and medical devices.Material Enhancements
Material science is another area where innovations are contributing to the growth of the 3D printing stainless steel market. Advances in stainless steel alloys, such as corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant formulations, have expanded the material’s applications. Manufacturers are also exploring hybrid materials that combine stainless steel with other metals to create composite materials with unique properties. These new materials offer enhanced strength, better resistance to extreme conditions, and improved fatigue performance, making 3D printing more attractive for industries requiring durable, high-performance components.Automation and Hybrid Manufacturing
Hybrid manufacturing systems that combine 3D printing with traditional subtractive processes (such as machining or milling) are also gaining traction in the stainless steel market. This hybrid approach enables manufacturers to print parts quickly and with high precision, followed by traditional processes to refine and finish the parts. The integration of automation further streamlines production, reduces costs, and improves efficiency. By automating the entire production cycle, companies can improve throughput and reduce human error, making the process more scalable for industrial applications.On-Demand Production
3D printing enables on-demand production, which is one of its most significant innovations. In industries such as aerospace and automotive, where supply chain flexibility and part customization are crucial, 3D printing allows manufacturers to produce stainless steel parts as needed, eliminating the need for large inventories. This reduces storage costs, ensures faster turnaround times, and helps companies respond to changes in demand or supply chain disruptions. As businesses continue to focus on efficiency and cost reduction, the demand for on-demand production will continue to rise, pushing further innovation in the sector.
Restraints Hindering Market Growth
High Initial Investment
Despite the advantages of 3D printing, one of the major restraints is the high initial investment required for industrial-grade 3D printers capable of working with stainless steel. These machines are costly, and the need for specialized software, skilled operators, and maintenance can add to the expense. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), as well as businesses in developing regions, may find it difficult to justify such significant investments, limiting the adoption of 3D printing technologies.Material Limitations
While 3D printing stainless steel has advanced in recent years, there are still material limitations to consider. The mechanical properties of 3D printed stainless steel parts, such as strength, ductility, and toughness, can sometimes fall short of traditionally manufactured components, particularly in critical applications like aerospace or medical implants. Post-processing is often required to improve the surface finish and mechanical properties, but this can add time and cost to the production process. The ongoing development of new materials and printing techniques is crucial for overcoming these limitations.Speed and Scalability
Although 3D printing provides significant advantages in terms of customization and complex geometries, the speed of production is still a concern for large-scale manufacturing. While advancements in printing speed are being made, the process can still be slower compared to traditional methods, especially for large parts or high-volume production. The scalability of 3D printing stainless steel remains a challenge, particularly for industries that require mass production of standardized parts. Innovations in speed, precision, and throughput are necessary to make 3D printing a viable option for large-scale manufacturing operations.Skilled Labor Shortage
The growing adoption of 3D printing in stainless steel production has led to an increased demand for skilled labor. Professionals with expertise in 3D design, machine operation, and post-processing are essential for maximizing the potential of 3D printing technologies. However, there is a shortage of such skilled workers, and companies may need to invest in training programs or hire specialized talent to fill the gap. This labor shortage could slow down the widespread adoption of 3D printing, particularly in regions where educational programs and training resources are limited.
Disruptions in the Market
Competitive Pressure and New Entrants
The 3D printing stainless steel market is experiencing growing competition from both established companies and new entrants. As technology becomes more accessible, a larger number of players are entering the market, offering innovative solutions and new business models. This increase in competition is driving down costs, increasing innovation, and leading to a more diverse range of product offerings. For example, companies specializing in low-volume, high-performance parts are challenging traditional manufacturers by offering highly customized solutions. This disruptive shift is likely to continue as new technologies emerge and more industries explore the potential of 3D printing.Supply Chain Resilience
The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the vulnerability of global supply chains, and industries are increasingly looking to 3D printing as a means of improving supply chain resilience. On-demand manufacturing, localized production, and the ability to quickly pivot to meet new demands are becoming key priorities. The potential of 3D printing to disrupt traditional supply chains by enabling decentralized production and reducing reliance on imports and large inventories is gaining traction. As businesses prioritize supply chain resilience, 3D printing could see a dramatic increase in adoption across multiple sectors.Regulatory and Standardization Issues
As 3D printing continues to grow, regulatory and standardization challenges are emerging. In industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare, where safety and performance are critical, regulations surrounding the use of 3D printed parts need to be clear and robust. The lack of established standards for 3D printing stainless steel parts could delay the widespread adoption of the technology in regulated industries. Ongoing efforts to develop industry-wide standards will be essential for mitigating these disruptions and ensuring the safe and effective use of 3D printed stainless steel components.
Conclusion
The 3D printing stainless steel market is experiencing transformative innovations that are shaping its future. Advancements in technology, materials, and automation are driving growth and opening up new opportunities across various industries. However, the market faces several restraints, including high initial costs, material limitations, and scalability challenges. Disruptions, such as increasing competition and shifts toward more resilient supply chains, are also influencing the market’s trajectory. Looking ahead, the continued development of 3D printing technologies, along with overcoming existing barriers, will be key to unlocking the full potential of stainless steel 3D printing and driving its widespread adoption.