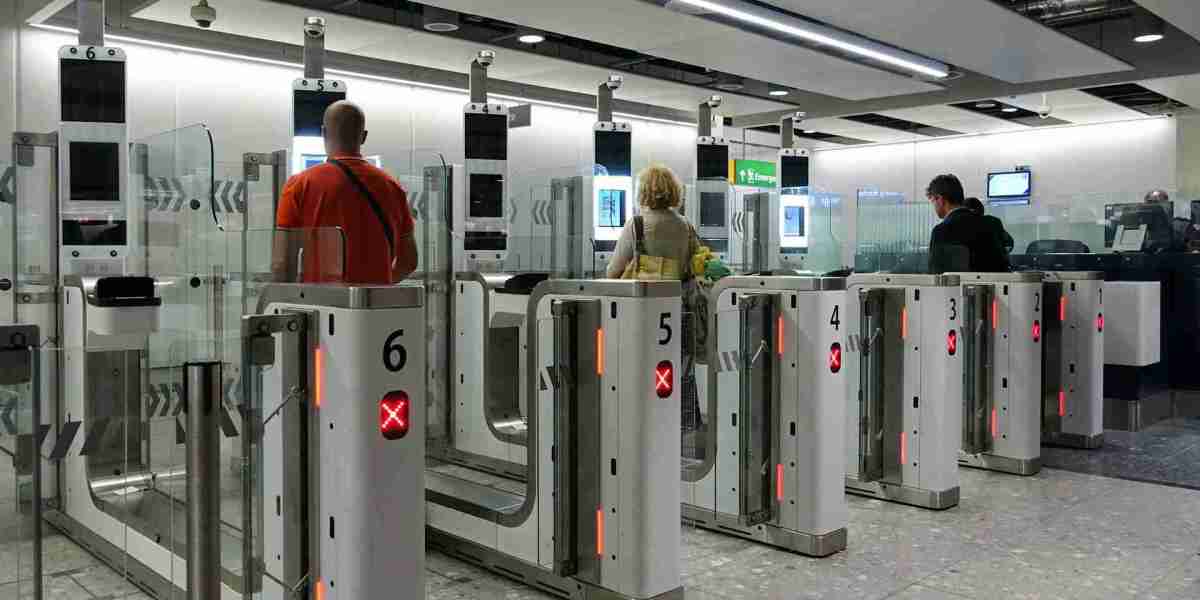
In recent years, the global automated border control market has gained significant momentum. This growth is driven by advancements in biometric technologies, the need for enhanced security measures, and growing international travel volumes. Automated Border Control (ABC) systems, which use biometrics and other identification technologies to facilitate passenger processing at borders, are revolutionizing the travel industry. However, understanding the market’s supply chain dynamics is crucial for stakeholders to fully capitalize on the opportunities emerging within this sector.
The Key Players in the Supply Chain
The supply chain for the automated border control market involves several players, ranging from technology developers to system integrators, and end-users like governments and airports. Key segments within this chain include:
Technology Providers: These companies are at the forefront of innovation in the ABC market. They provide the necessary hardware, software, and biometric solutions that power automated border control systems. Companies like NEC Corporation, Thales Group, and Idemia are leaders in biometric technologies such as facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and iris recognition, which are integral components of ABC systems.
System Integrators: These firms are responsible for combining the various technologies into a cohesive automated border control solution. They work with technology providers to customize systems according to the specific needs of each border facility. Some system integrators specialize in the integration of biometric systems with legacy systems at airports, making the transition to ABC smoother and more efficient.
Governments and Regulatory Bodies: Governments are the primary customers in the automated border control market. They set the regulatory standards and guidelines for the implementation of automated systems at borders and airports. As national security becomes a more pressing issue globally, governments are pushing for more automated, secure, and efficient border control measures.
Airports and Border Agencies: These end-users implement ABC systems at physical border locations, such as airports, seaports, and land borders. They are responsible for maintaining and operating the systems, ensuring that travelers are processed efficiently while adhering to security protocols.
Travelers: Though not a direct player in the supply chain, the traveler is a key beneficiary of the ABC system. With seamless biometric authentication, travelers enjoy faster and more secure border processing.
Market Challenges and Opportunities
The automation of border control systems presents several challenges and opportunities within the supply chain.
Challenges:
- Security and Privacy Concerns: The use of biometric data raises significant privacy issues, especially regarding data protection and misuse. This concerns consumers and regulatory bodies alike, creating hurdles in implementing automated systems.
- High Initial Costs: The setup and installation of automated border control systems require substantial initial investments, especially for governments of developing nations or smaller airports that have limited budgets.
- System Integration Complexity: Integrating new automated systems with existing infrastructure in airports and borders can be complex, requiring expertise in both new technologies and legacy systems.
Opportunities:
- Advancements in Biometrics: As biometric technologies improve, automated systems are becoming more efficient and reliable. Facial recognition, for example, is expected to increase in adoption due to its non-intrusive nature and high accuracy.
- Growing Demand for Border Security: As global travel increases and security concerns escalate, the demand for faster, more secure border control measures is expected to rise. This is a huge opportunity for companies in the ABC supply chain to expand their offerings.
- Collaborations and Partnerships: Strategic partnerships between technology providers and government bodies could streamline the adoption process, making ABC systems more accessible globally.
Supply Chain Innovations and Future Outlook
As the market continues to evolve, there are several key trends shaping its future supply chain dynamics. For example, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in automated border control is becoming more prominent. AI-powered systems can enhance biometric matching and improve overall system efficiency by learning and adapting to various border environments. Furthermore, the rise of cloud computing is enabling border control agencies to manage vast amounts of data more efficiently.
Another significant shift in the supply chain is the growing role of public-private partnerships (PPPs). Many governments are turning to PPPs to accelerate the implementation of automated border systems without bearing the full financial burden. This collaboration can also spur innovation, as private sector companies bring cutting-edge technologies to the table, while public agencies ensure regulatory compliance and security.
Conclusion
The automated border control market presents a rapidly evolving landscape for businesses, governments, and travelers. As demand for faster, more secure border crossings grows, supply chain players must work in unison to meet this need. While challenges remain, particularly around privacy concerns and integration complexities, the opportunities in this market are abundant. With advancements in biometrics, AI, and cloud computing, the automated border control market is poised for significant growth, offering greater efficiency and security at border points worldwide.