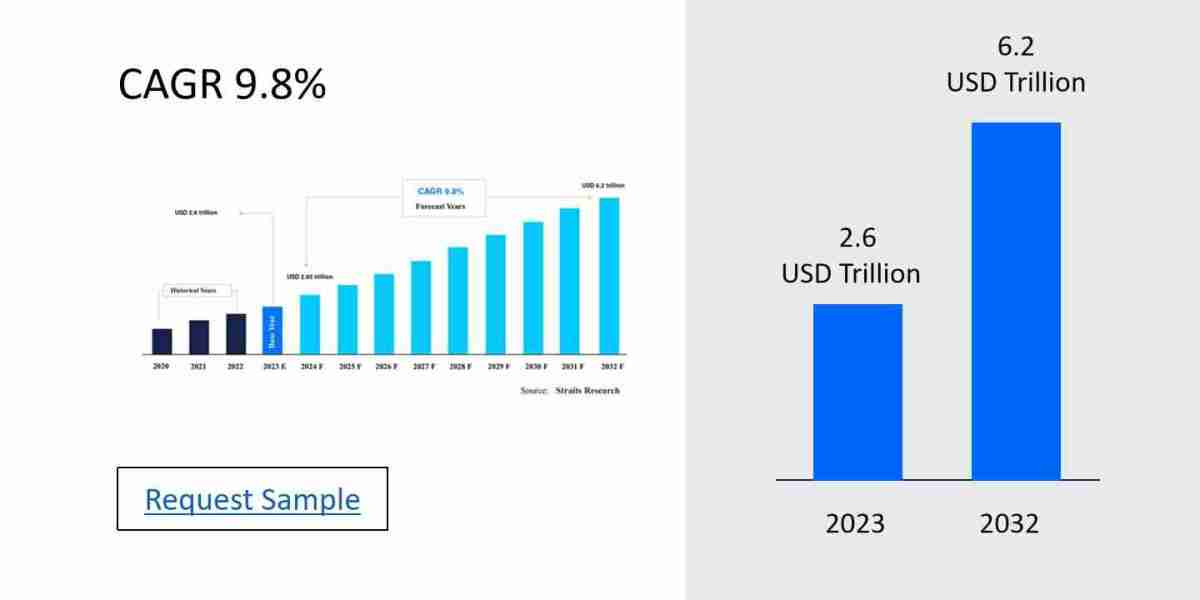
The dry yeast market has grown considerably as its applications expand across multiple industries, from baking to brewing and beyond. Yeast is essential in many processes, especially fermentation, and is available in various forms, each suited to different production needs. Among the most popular types are active dry yeast (ADY) and instant dry yeast (IDY), both of which have become staples in both commercial and home kitchens. However, despite their similar appearance and primary function, these two yeast varieties have distinct characteristics and are used differently depending on the application.
As consumers and manufacturers continue to demand more convenient, efficient, and cost-effective products, innovations in the dry yeast market are helping meet these needs. Both active dry yeast and instant dry yeast are at the forefront of these innovations, but their unique properties influence how they are utilized in different contexts.
Understanding Active Dry Yeast
Active dry yeast is one of the oldest and most widely used types of dry yeast. It is produced by drying a liquid culture of yeast cells to preserve their ability to ferment. The yeast cells in ADY are dormant and must be rehydrated before use, which often requires dissolving the yeast in warm water to activate it. Once rehydrated, ADY can be added to dough or other food products for fermentation.
Active dry yeast is often favored in traditional baking applications, where long fermentation times and slower rises are desired. It is commonly used in bread making, where its rehydration step allows bakers to control the fermentation process carefully. Its slightly slower fermentation speed can enhance the flavor and texture of certain baked goods, particularly artisan breads.
Exploring Instant Dry Yeast
Instant dry yeast, often referred to as quick-rise or rapid-rise yeast, is similar to ADY in its production but with a key difference. Unlike ADY, instant dry yeast does not require rehydration before use. It can be mixed directly with dry ingredients, making it more convenient for many applications. This difference in formulation is due to the fact that the yeast cells in IDY are smaller and contain a higher percentage of live cells compared to ADY, which allows them to activate more quickly.
Instant dry yeast is particularly popular in high-volume commercial baking environments where speed and efficiency are critical. Its fast fermentation time makes it ideal for processes that require a quick rise, such as in industrial bread production, pizza dough, and other quick-baking goods. The ability to mix IDY directly with dry ingredients speeds up production, reduces labor time, and increases overall efficiency. For home bakers, IDY is also a convenient choice, as it eliminates the need for yeast activation, simplifying the baking process.
Comparing the Two: Applications in the Dry Yeast Market
While both active dry yeast and instant dry yeast serve the same fundamental purpose—fermenting dough and other food products—their differing characteristics make them better suited to certain applications. For traditional, slow-rise bread recipes, ADY is often the preferred option due to its ability to develop more complex flavors during extended fermentation periods. This makes it ideal for artisanal breads and pastries that benefit from a slower rise and deeper flavor profiles.
On the other hand, IDY's quick activation and faster fermentation process make it better suited for commercial applications where efficiency and speed are paramount. Its use in large-scale bakery production and quick-serve establishments is growing, particularly for products like pizzas, rolls, and other baked goods that require rapid processing. The ability to incorporate IDY into recipes without pre-activation is also attractive to home bakers looking for a more streamlined approach to baking.
Market Innovations and Trends
In recent years, the dry yeast market has witnessed several innovations aimed at improving both the functionality and sustainability of yeast products. One such trend is the development of organic and non-GMO dry yeast. As consumers become increasingly concerned with the quality and sourcing of ingredients, there is a growing demand for clean-label yeast products. Manufacturers are responding to this trend by offering ADY and IDY that are certified organic, non-GMO, and free from artificial additives. These products cater to the increasing number of consumers seeking natural and sustainably produced ingredients.
Challenges in the Dry Yeast Market
Despite the positive trends and innovations in the dry yeast market, there are challenges that manufacturers must overcome. One key challenge is the inconsistency in raw material quality, which can impact the fermentation process and the overall performance of yeast. Furthermore, climate change and supply chain disruptions can affect the availability of the raw materials used to grow yeast, potentially leading to supply shortages and price fluctuations.