The stationary fuel cell systems market is undergoing a transformative phase driven by the global shift towards sustainable and clean energy solutions. As governments, industries, and consumers increasingly seek ways to reduce carbon emissions and enhance energy efficiency, fuel cells present a compelling option for decentralized power generation. For new players aiming to enter this dynamic sector, understanding key trends and identifying avenues for growth is essential to gaining a foothold and succeeding in the competitive landscape.
The Rise of Fuel Cell Technologies
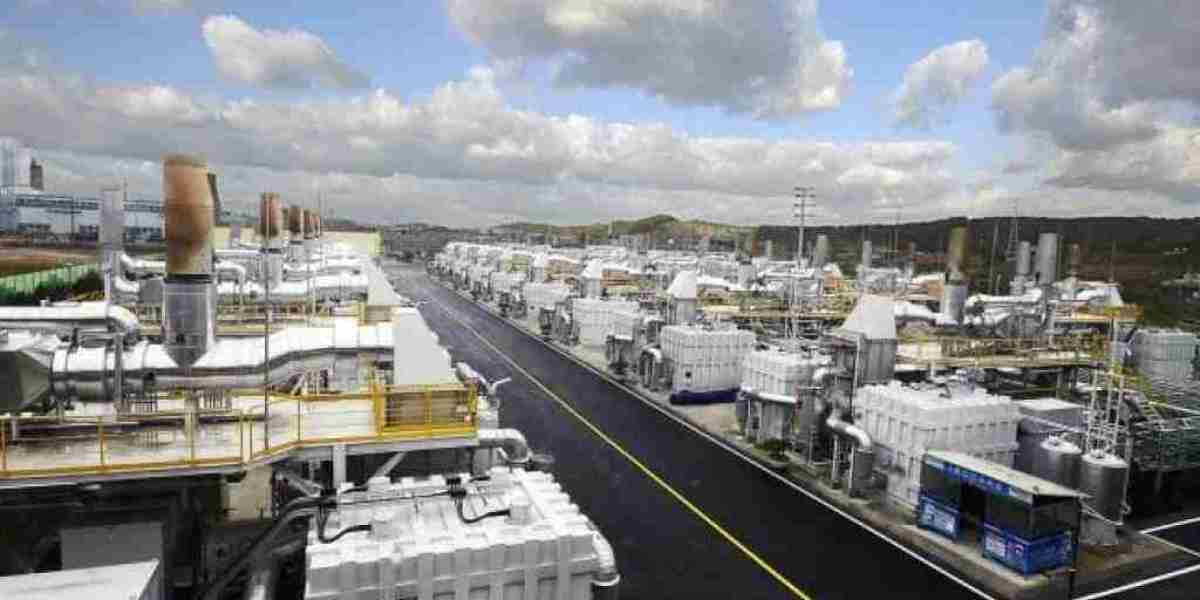
Fuel cells, which generate electricity through electrochemical reactions rather than combustion, offer significant advantages in terms of efficiency, emissions, and reliability. Stationary fuel cell systems are being deployed for a variety of applications, including backup power, distributed generation, and remote energy solutions. These systems are increasingly being viewed as vital components in the global transition to renewable energy, where they complement other clean technologies such as solar and wind power.
Fuel cells are particularly attractive due to their ability to run on hydrogen and other alternative fuels, creating a pathway for decarbonizing sectors such as manufacturing, transportation, and residential energy supply. This technology’s ability to deliver stable and continuous power without relying on the grid is also a key selling point for areas with unreliable electricity supply.
For new market entrants, the growing demand for cleaner energy presents an opportunity to position themselves at the forefront of an evolving industry. With government incentives and supportive policies aimed at reducing fossil fuel dependency, now is an optimal time for new players to explore the stationary fuel cell systems market.
Key Growth Drivers for Emerging Players
Several key factors are contributing to the growth of the stationary fuel cell market, making it an attractive space for new entrants:
Government Regulations and Incentives: Governments worldwide are implementing stringent regulations to curb emissions and promote sustainable energy sources. This regulatory push is propelling the demand for renewable energy systems, including fuel cells. Incentives such as tax credits, subsidies, and research grants for fuel cell development and installation are lowering the entry barriers for new companies.
Rising Environmental Awareness: As concerns over climate change intensify, consumers and businesses alike are becoming more conscious of their environmental footprint. This has led to a surge in demand for green energy solutions, including hydrogen-powered stationary fuel cells. By offering products that align with eco-friendly goals, new players can appeal to both residential and commercial sectors looking to make the switch to cleaner energy.
Technological Advancements: Recent technological improvements have significantly enhanced the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and scalability of stationary fuel cell systems. As fuel cell technology continues to evolve, the cost of production is expected to decrease, creating greater market accessibility. For new companies, these advancements present a window of opportunity to innovate and bring competitive solutions to market.
Corporate Sustainability Initiatives: Corporations are increasingly prioritizing sustainability in their operations, with many committing to net-zero emissions targets. This shift is creating a demand for energy solutions that can deliver reliable power while reducing carbon emissions. Fuel cells, with their ability to produce power with minimal environmental impact, are poised to play a critical role in meeting corporate sustainability goals, offering a lucrative market for new entrants.
Navigating the Competitive Landscape
While the potential for growth is significant, the stationary fuel cell systems market is not without its challenges. Established players with deep pockets, strong brand recognition, and extensive R&D capabilities dominate much of the market. New companies must find ways to differentiate themselves and overcome these hurdles to establish a competitive edge.
Partnerships and Collaborations: One viable strategy for new entrants is to forge strategic partnerships with established industry leaders. Collaborating with larger companies, utilities, or even government bodies can provide access to funding, technical expertise, and distribution channels that may be difficult to secure independently. For example, joining forces with hydrogen production companies or clean energy innovators could allow new players to offer integrated solutions that cater to the growing demand for decarbonized power sources.
Innovative Solutions and Niche Markets: Another route to success is by focusing on innovation or targeting niche market segments. New companies should look for areas within the fuel cell space that are underserved or could benefit from tailored solutions. For instance, fuel cells tailored to backup power needs in critical sectors like healthcare or data centers can meet the demand for reliable and efficient energy in high-stakes environments. Additionally, localized or off-grid fuel cell systems that cater to remote or island communities could serve as a differentiated offering, addressing energy access issues.