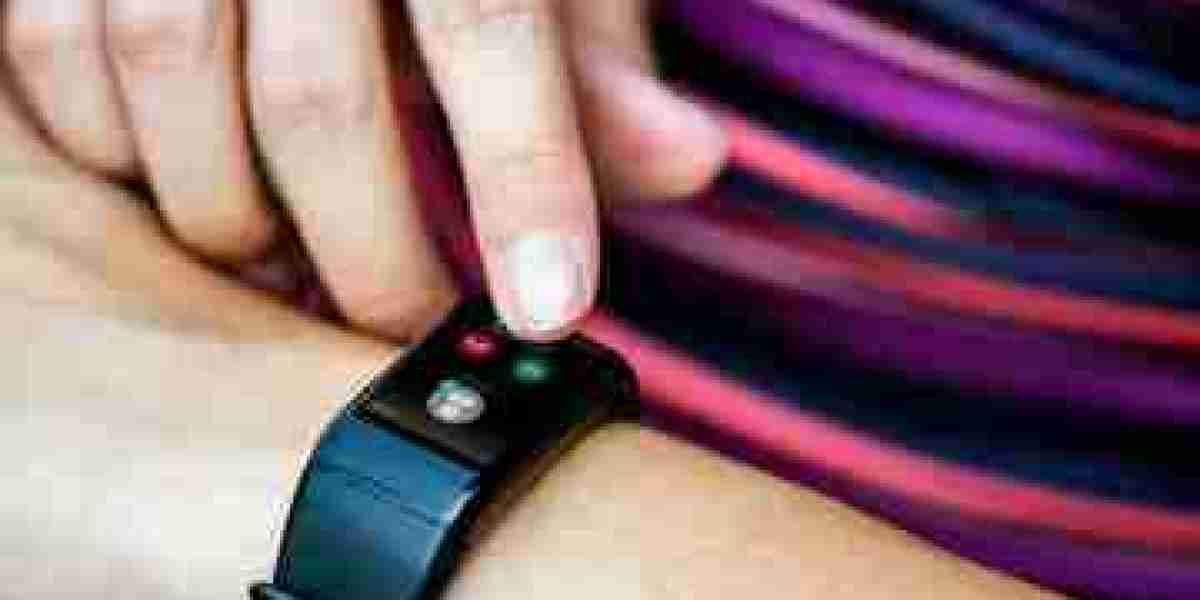
Wearable payment technology is transforming digital transactions, offering users a seamless and contactless way to pay via smartwatches, fitness bands, and other connected wearables. This innovation provides convenience and speed, making payments faster and more secure. However, despite its potential, several barriers prevent widespread adoption and expansion of wearable payments. These challenges include security concerns, high costs, limited infrastructure, regulatory hurdles, and consumer skepticism. This article explores the key barriers affecting the wearable payments market and how they impact growth.
1. Security and Fraud Concerns
Security remains a significant barrier to the adoption of wearable payments. Consumers worry about data breaches, fraud, and unauthorized transactions. Although encryption, tokenization, and biometric authentication enhance security, cybercriminals continue to develop sophisticated hacking methods.
Additionally, lost or stolen wearable devices pose risks if they lack proper security features like PIN protection or biometric authentication. Overcoming these security concerns is crucial for boosting consumer trust and adoption.
2. High Cost of Wearable Payment Devices
One of the primary barriers to mass adoption is the high price of wearable payment devices. Smartwatches and other payment-enabled wearables are often expensive, making them inaccessible to budget-conscious consumers. Even lower-cost wearables may lack advanced security features or compatibility with multiple payment networks.
To overcome this barrier, manufacturers must reduce production costs while maintaining high security and usability standards. Affordable wearable payment options will encourage more consumers to embrace this technology.
3. Limited Merchant Acceptance and Infrastructure
Although contactless payments are becoming more common, many businesses still do not support wearable payment transactions. Small retailers and merchants in developing regions may lack NFC-enabled point-of-sale (POS) terminals, making it difficult for consumers to rely solely on wearable payments.
If businesses do not invest in upgrading their payment infrastructure, wearable payments will struggle to gain widespread acceptance. Expanding merchant adoption of contactless payments is essential for market growth.
4. Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
The wearable payments market is subject to complex financial regulations that vary by region. Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) in the U.S. impose strict compliance requirements.
Meeting these regulatory standards adds complexity and costs for businesses developing wearable payment solutions. Inconsistent regulations across different markets further slow down global expansion. Addressing these challenges requires greater collaboration between regulatory bodies and fintech companies.
5. Consumer Skepticism and Lack of Awareness
Many consumers are unfamiliar with how wearable payments work or are skeptical about their security and reliability. Concerns about privacy, data collection, and potential misuse deter people from adopting wearable payment technology.
To address this barrier, companies must invest in educational campaigns to inform consumers about the benefits, security measures, and ease of use of wearable payments. Increasing awareness and trust is key to driving adoption.
6. Battery Life and Reliability Issues
Unlike traditional payment methods, wearable payment devices depend on battery power. If a device runs out of charge, it becomes useless for transactions. This limitation reduces reliability and convenience, especially for users who rely on wearable payments for daily purchases.
Improving battery life and energy efficiency in wearable payment devices is crucial for ensuring a seamless user experience.
7. Interoperability and Compatibility Issues
A fragmented ecosystem of wearable payment platforms creates compatibility challenges. Different manufacturers use proprietary operating systems and payment protocols, making it difficult for consumers to switch between devices or link multiple payment services.
For example, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay each operate within separate ecosystems, limiting interoperability. Standardizing payment protocols across wearable devices would enhance user experience and adoption rates.
8. Dependence on Smartphones and Connectivity
Many wearable payment devices require a smartphone connection or internet access to function properly. If a user’s smartphone is not nearby or the device loses connectivity, transactions may not go through.
This dependence on external devices reduces the practicality of wearables as standalone payment solutions. Ensuring that wearable payments can work offline or independently of smartphones will help drive adoption.
9. Economic Uncertainty and Financial Barriers
Economic downturns and financial instability can impact consumer spending and investment in new technologies. When people face financial uncertainty, they may be hesitant to purchase smartwatches or other payment-enabled wearables.
Additionally, businesses may delay upgrading their payment systems during economic slowdowns. Economic fluctuations can slow market expansion and delay technological advancements in wearable payments.
10. Competition from Other Digital Payment Methods
Wearable payments compete with mobile wallets, QR code payments, and traditional contactless cards. Many consumers already use smartphones for digital transactions, reducing the perceived need for wearable payment devices.
To differentiate themselves, wearable payment providers must offer unique benefits such as enhanced security, better convenience, and additional functionalities beyond payments. Without clear advantages, wearable payments may struggle to compete with existing digital payment solutions.
Conclusion
Despite its promising potential, the wearable payments market faces several barriers that limit its widespread adoption and growth. Security concerns, high costs, limited merchant acceptance, regulatory hurdles, and consumer skepticism remain major obstacles. Additionally, issues related to battery life, interoperability, smartphone dependency, economic uncertainty, and competition further challenge the market.
To overcome these barriers, industry leaders must focus on improving security, lowering costs, expanding merchant adoption, and enhancing consumer education. By addressing these challenges, wearable payments can become a dominant force in the future of digital transactions.