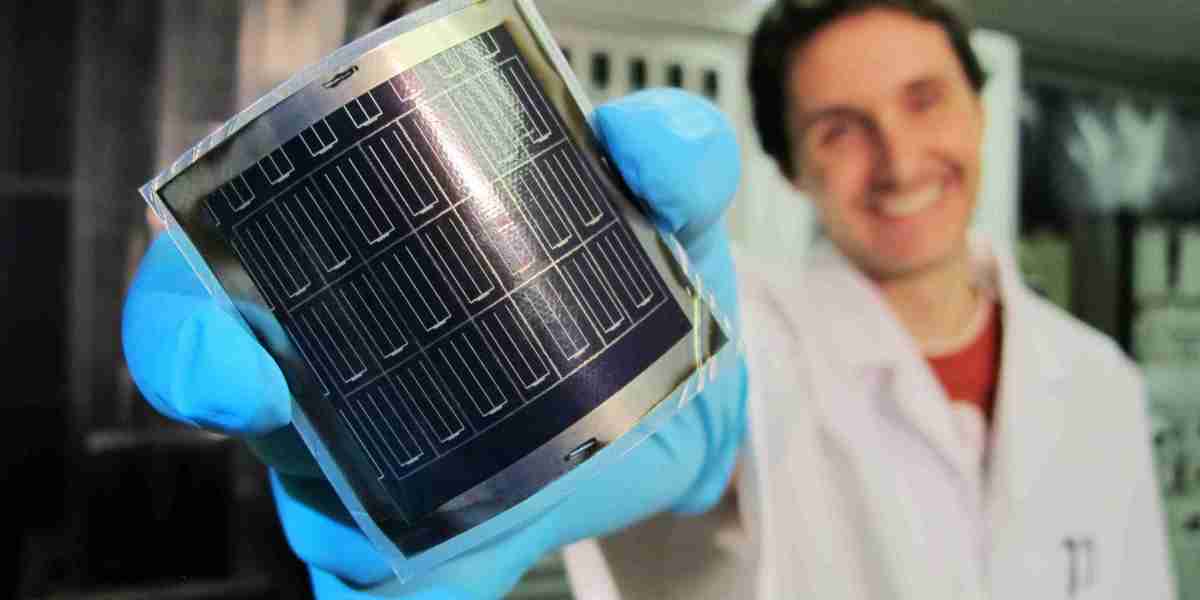
In recent years, the focus on renewable energy sources has intensified due to the ever-increasing need for sustainable energy solutions. Among the various innovations in solar energy technology, polymer solar cells (PSCs) have garnered significant attention. These cells are considered to be cost-effective and flexible alternatives to traditional silicon-based solar panels. However, despite their promising potential, the Polymer Solar Cells Market still faces a variety of entry barriers that hinder broader adoption and commercialization. This article delves into the major obstacles preventing greater growth in this market.
Technological Challenges
One of the primary barriers to the entry of polymer solar cells into the market is their technological limitations. PSCs, while advantageous in terms of flexibility and manufacturing processes, still suffer from lower efficiency levels compared to their silicon counterparts. The power conversion efficiency (PCE) of PSCs remains a key concern, as it directly impacts their feasibility for widespread commercial use. Despite ongoing research and development, the stability of polymer-based materials under prolonged exposure to environmental conditions remains another challenge. This lower durability compared to conventional solar cells further limits PSCs' ability to compete in long-term, large-scale energy projects.
Manufacturing Complexities
Another barrier relates to the complexities associated with manufacturing polymer solar cells. The production processes for PSCs involve intricate techniques such as solution-based printing and roll-to-roll processing. While these methods are often more cost-effective than traditional silicon-based solar panel manufacturing, scaling them up for large-scale production can be difficult. Manufacturing polymer solar cells at an industrial scale while maintaining high-quality standards poses several challenges. Moreover, producing these cells with consistent efficiency and yield remains a significant hurdle in achieving competitive market prices.
Limited Market Awareness and Adoption
The polymer solar cells market faces a crucial barrier in the form of limited market awareness. While there is significant excitement among scientists and researchers regarding the potential of PSCs, there is still a lack of consumer understanding about the benefits and capabilities of these cells. Traditional silicon-based solar cells have been the dominant technology for decades, making it difficult for polymer solar cells to overcome the trust deficit in the market. In addition, energy companies and developers tend to prefer proven, reliable technologies due to the substantial financial investments and risks associated with energy infrastructure.
Supply Chain Limitations
For polymer solar cells to achieve widespread commercialization, robust and efficient supply chains are essential. The production of PSCs relies on specific raw materials and organic polymers that are not yet available in the volume necessary to meet potential global demand. Supply chain bottlenecks and limited access to high-quality, cost-effective materials could delay large-scale market entry. Furthermore, ensuring the availability of specialized components for PSC assembly is a critical challenge for manufacturers, especially when considering international distribution and logistics.
Policy and Regulatory Uncertainty
The adoption of any new technology is highly influenced by governmental policies and regulations. In the case of polymer solar cells, a lack of clear and supportive regulatory frameworks poses a significant challenge to market entry. Different countries have varied energy policies, and there is currently no universal standard for the certification or accreditation of PSCs. The absence of consistent governmental incentives, subsidies, or tax benefits for the development and deployment of polymer-based solar energy systems has created uncertainty for potential investors. The complexity and slowness in regulatory approvals further hinder the commercialization process.
Conclusion
The polymer solar cells market holds enormous potential, but several factors hinder its progress. Overcoming these entry barriers, such as improving efficiency and stability, simplifying the manufacturing process, raising consumer awareness, developing reliable supply chains, and establishing clear policies, will be key to the successful commercialization of polymer solar cells. While challenges remain, ongoing research, investment in technology, and collaboration among key stakeholders may eventually pave the way for widespread adoption of PSCs in the global energy market.