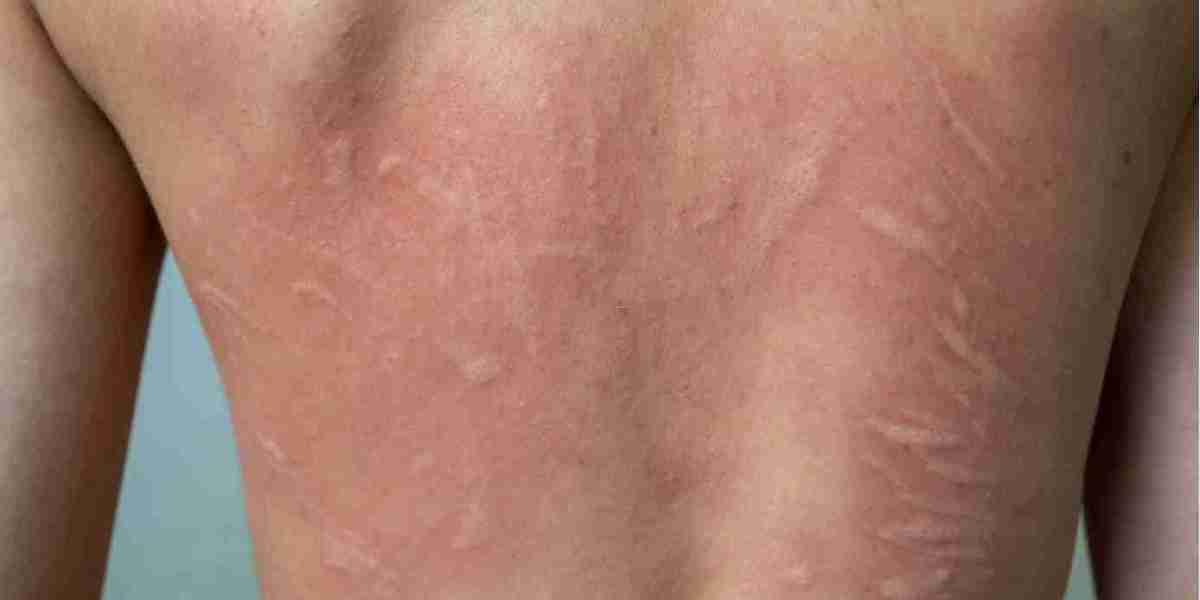
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by raised, itchy welts that can appear suddenly and disappear within hours or days. It can be triggered by various factors, including allergies, stress, environmental changes, or underlying health conditions. While medical treatments like antihistamines or, in some cases, antibiotics such as cephalexin (often sourced from reliable suppliers for managing bacterial infections that may exacerbate symptoms) are used to control urticaria, many wonder if lifestyle changes can prevent or reduce its occurrence.
Understanding Urticaria and Its Triggers
Urticaria occurs when the body releases histamine, causing blood vessels to leak fluid into the skin, resulting in welts. It can be acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (persisting longer). Common triggers include:
Allergens: Foods (e.g., nuts, shellfish), pollen, pet dander, or insect bites.
Physical Triggers: Heat, cold, pressure, sunlight, or exercise.
Stress: Emotional or physical stress can exacerbate symptoms.
Medications: Certain drugs, including some antibiotics or painkillers.
Infections: Viral or bacterial infections may contribute to hives.
Environmental Factors: Chemicals, fragrances, or synthetic fabrics.
While medical interventions, such as ceftriaxone injections distributors for severe infections linked to urticaria), can address underlying causes, lifestyle changes can play a significant role in prevention by reducing exposure to triggers and supporting overall health.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Urticaria
1. Identify and Avoid Triggers
The first step in preventing urticaria is identifying personal triggers. Keeping a detailed diary of flare-ups, including foods eaten, activities, and environmental exposures, can help pinpoint causes. For example:
Food Allergies: Common culprits include dairy, eggs, peanuts, and shellfish. If food allergies are suspected, consult an allergist for testing and eliminate trigger foods. Opt for a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish or flaxseed).
Environmental Control: Avoid known allergens like pollen by staying indoors during high pollen seasons or using air purifiers. Choose hypoallergenic bedding and clothing made of natural fibers like cotton to reduce skin irritation.
2. Manage Stress Effectively
Stress is a well-documented trigger for urticaria. Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making the body more reactive to histamine release. Incorporating stress-reducing practices can help:
Mindfulness and Meditation: Daily meditation or deep-breathing exercises can lower cortisol levels, reducing the likelihood of stress-induced hives.
Exercise: Moderate activities like yoga or walking can alleviate stress and improve circulation, but avoid overexertion, as excessive sweating or heat can trigger physical urticaria in some individuals.
Sleep Hygiene: Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep nightly. Poor sleep can increase stress and inflammation, worsening urticaria.
3. Optimize Skin Care
Proper skin care can minimize irritation and prevent urticaria flare-ups, especially for those with sensitive skin or physical triggers:
Gentle Products: Use fragrance-free, hypoallergenic soaps, moisturizers, and detergents. Harsh chemicals or dyes in personal care products can provoke hives.
Temperature Regulation: Avoid hot showers or baths, as heat can trigger urticaria. Lukewarm water and mild cleansers are gentler on the skin.
Moisturize Regularly: Dry skin can exacerbate itching. Apply a fragrance-free moisturizer daily to maintain the skin barrier.
4. Adopt an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Diet plays a crucial role in managing inflammation, which can influence urticaria. While specific food triggers vary, a diet that reduces systemic inflammation may help:
Include Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and turmeric, can reduce inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids from sources like salmon or walnuts may also help.
Limit Processed Foods: Sugary, processed, or high-fat foods can increase inflammation, potentially worsening urticaria.
Stay Hydrated: Drinking adequate water supports skin health and helps flush out toxins that could contribute to allergic reactions.
5. Strengthen Immunity
A robust immune system can reduce the likelihood of urticaria caused by infections or overreactions to allergens. While antibiotics like cephalexin from trusted suppliers can treat bacterial infections linked to hives, lifestyle changes can bolster immunity naturally:
Nutrient-Rich Diet: Ensure adequate intake of vitamins C, D, and zinc, which support immune function. Citrus fruits, fatty fish, and nuts are excellent sources.
Probiotics: Gut health influences immunity. Incorporate probiotic-rich foods like yogurt or kefir to promote a healthy gut microbiome.
Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Both can weaken immunity and increase inflammation, potentially triggering urticaria.
6. Environmental and Lifestyle Adjustments
Certain environmental factors can provoke urticaria, and small changes can make a big difference:
Temperature Control: For those with cold- or heat-induced urticaria, dress appropriately for the weather and avoid extreme temperatures. For example, wear loose, breathable clothing in hot weather to prevent overheating.
Chemical Exposure: Minimize contact with irritants like perfumes, cleaning agents, or synthetic fabrics. Opt for natural, hypoallergenic alternatives.
Exercise Caution: For individuals with exercise-induced urticaria, choose low-impact activities and avoid exercising in extreme heat or humidity.
7. Regular Medical Checkups
While lifestyle changes are effective, regular consultations with a healthcare provider are essential, especially for chronic urticaria. Underlying conditions like thyroid disorders or infections may contribute to hives. In cases where infections are a factor, treatments like ceftriaxone injections, sourced from wholesale providers for severe cases, may be prescribed. Routine checkups can also ensure timely adjustments to any treatment plan.
Limitations of Lifestyle Changes
While lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce urticaria flare-ups, they may not eliminate the condition entirely, especially in chronic cases or when triggers are unavoidable (e.g., pollen during allergy season). Genetic predispositions or underlying medical conditions may require additional interventions, such as antihistamines or, in rare cases, immunosuppressive therapies. Always consult a healthcare provider before making significant lifestyle changes, especially if taking medications like cephalexin for related infections.
Practical Tips for Implementation
Start Small: Gradually introduce changes, such as eliminating one trigger food at a time or adding a 10-minute meditation session daily.
Track Progress: Use a journal to monitor symptoms and identify which changes are most effective.
Seek Support: Work with a dermatologist, allergist, or nutritionist to create a personalized prevention plan.
Stay Consistent: Consistency is key to seeing results. Stick to routines like stress management or skin care for long-term benefits.
Conclusion
Urticaria can be a frustrating condition, but lifestyle changes offer a proactive way to prevent and manage flare-ups. By identifying triggers, managing stress, optimizing diet, and maintaining proper skin care, individuals can reduce the frequency and severity of hives. While medical treatments, including antibiotics from reliable cephalexin suppliers or ceftriaxone injections from wholesale sources for infection-related cases, can address underlying causes, lifestyle modifications empower individuals to take control of their health. With a combination of awareness, discipline, and professional guidance, urticaria can often be managed effectively, improving quality of life.